Page 346 - ACFE Fraud Reports 2009_2020
P. 346
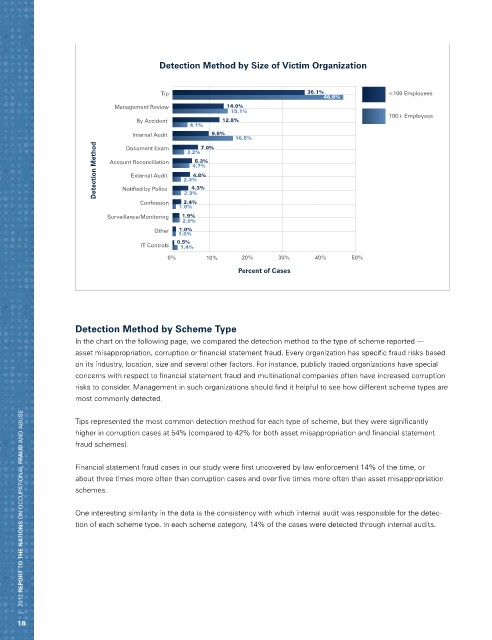
Detection Method by Size of Victim Organization
Tip 36.1% <100 Employees
46.6%
Management Review 14.0%
15.1%
100+ Employees
By Accident 12.8%
4.1%
Internal Audit 9.9%
16.5%
Detection Method Account Reconciliation 2.3% 4.8%
Document Exam
7.0%
3.2%
5.3%
4.7%
External Audit
4.3%
Notified by Police
2.3%
Confession 2.4%
1.0%
Surveillance/Monitoring 1.9%
2.0%
Other 1.0%
1.0%
0.5%
IT Controls 1.4%
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50%
Percent of Cases
Detection Method by Scheme Type
In the chart on the following page, we compared the detection method to the type of scheme reported —
asset misappropriation, corruption or financial statement fraud. Every organization has specific fraud risks based
on its industry, location, size and several other factors. For instance, publicly traded organizations have special
concerns with respect to financial statement fraud and multinational companies often have increased corruption
risks to consider. Management in such organizations should find it helpful to see how different scheme types are
most commonly detected.
| 2012 REPORT TO THE NATIONS on occupational FRAUD and abuse
Tips represented the most common detection method for each type of scheme, but they were significantly
higher in corruption cases at 54% (compared to 42% for both asset misappropriation and financial statement
fraud schemes).
Financial statement fraud cases in our study were first uncovered by law enforcement 14% of the time, or
about three times more often than corruption cases and over five times more often than asset misappropriation
schemes.
One interesting similarity in the data is the consistency with which internal audit was responsible for the detec-
tion of each scheme type. In each scheme category, 14% of the cases were detected through internal audits.
18