Page 1275 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1275
1250 CHAPTER 12
VetBooks.ir 12.43 BACTERIAL OR FUNGAL FOLLICULITIS
AND FURUNCULOSIS (ACNE)
Definition/overview
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicle with an
accumulation of inflammatory cells within the follicu-
lar lumen. It can be caused by bacteria, fungi and rarely
equine demodicosis. As the infective process proceeds,
degeneration of the hair follicle leads to infection of
the surrounding dermis and subcutis (furunculosis)
(Fig. 12.44). Where multiple infection sites coalesce,
a carbuncle or a boil is formed. These occur in horses
with saddle boils, heat rash (Staphylococcus spp.), cheek
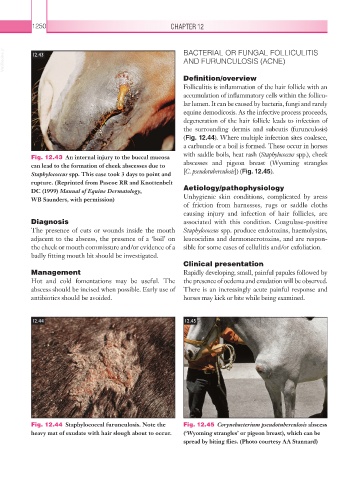
Fig. 12.43 An internal injury to the buccal mucosa
can lead to the formation of cheek abscesses due to abscesses and pigeon breast (Wyoming strangles
Staphylococcus spp. This case took 3 days to point and [C. pseudotuberculosis]) (Fig. 12.45).
rupture. (Reprinted from Pascoe RR and Knottenbelt
DC (1999) Manual of Equine Dermatology, Aetiology/pathophysiology
WB Saunders, with permission) Unhygienic skin conditions, complicated by areas
of friction from harnesses, rugs or saddle cloths
causing injury and infection of hair follicles, are
Diagnosis associated with this condition. Coagulase-positive
The presence of cuts or wounds inside the mouth Staphylococcus spp. produce endotoxins, haemolysins,
adjacent to the abscess, the presence of a ‘boil’ on leucocidins and dermonecrotoxins, and are respon-
the cheek or mouth commissure and/or evidence of a sible for some cases of cellulitis and/or exfoliation.
badly fitting mouth bit should be investigated.
Clinical presentation
Management Rapidly developing, small, painful papules followed by
Hot and cold fomentations may be useful. The the presence of oedema and exudation will be observed.
abscess should be incised when possible. Early use of There is an increasingly acute painful response and
antibiotics should be avoided. horses may kick or bite while being examined.
12.44 12.45
Fig. 12.44 Staphylococcal furunculosis. Note the Fig. 12.45 Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis abscess
heavy mat of exudate with hair slough about to occur. (‘Wyoming strangles’ or pigeon breast), which can be
spread by biting flies. (Photo courtesy AA Stannard)