Page 689 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 689
664 CHAPTER 3
VetBooks.ir is often less significant and anaerobic infection is airway, especially the nasopharynx, can cause dys-
pnoea and an abnormal respiratory noise. The dis-
often more relevant.
Clinical presentation ease almost invariably has a chronic history, which
can vary from unilateral discharge despite treat-
A unilateral, or predominantly unilateral, purulent ment, through to intermittent unilateral discharge
nasal discharge is almost invariably the presenting for over 1 year.
sign. Swelling in the parotid region is conceivable,
as distension of the pouch is frequent, but is seldom Differential diagnosis
noted clinically. Distension of the pouch into the The primary differential diagnosis is sinusitis. Most
cases have been treated with a presumptive diagnosis
of sinusitis for a period. Discharge from the lower
3.114
airway, which can be quite purulent, can occasion-
ally appear down one nostril and create the incorrect
impression of a URT disease.
Diagnosis
Endoscopy usually provides a definitive diagnosis.
Endoscopic examination of the nasophayrnx may
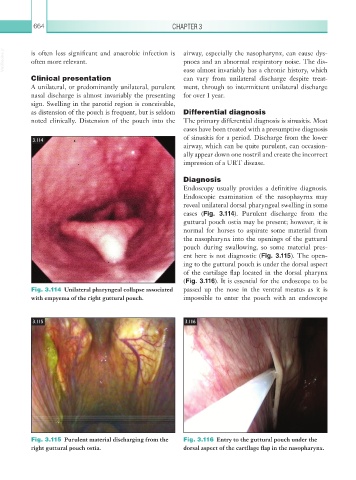
reveal unilateral dorsal pharyngeal swelling in some
cases (Fig. 3.114). Purulent discharge from the
guttural pouch ostia may be present; however, it is
normal for horses to aspirate some material from
the nasopharynx into the openings of the guttural
pouch during swallowing, so some material pres-
ent here is not diagnostic (Fig. 3.115). The open-
ing to the guttural pouch is under the dorsal aspect
of the cartilage flap located in the dorsal pharynx
(Fig. 3.116). It is essential for the endoscope to be
Fig. 3.114 Unilateral pharyngeal collapse associated passed up the nose in the ventral meatus as it is
with empyema of the right guttural pouch. impossible to enter the pouch with an endoscope
3.115 3.116
Fig. 3.115 Purulent material discharging from the Fig. 3.116 Entry to the guttural pouch under the
right guttural pouch ostia. dorsal aspect of the cartilage flap in the nasopharynx.