Page 690 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 690
Respir atory system: 3.2 Surgical conditions of the respir atory tr act 665
VetBooks.ir in the middle nasal meatus. Once in the pouch vis- 3.117
ibility is often quite obscured by purulent material.
The lining of the pouch is markedly thickened, lim-
iting identification of normal structures (Fig. 3.117).
Opening the pouch will often result in a flow of fluid
from the ostia but the ventral aspect of the pouch is
almost invariably obscured. The contralateral pouch
can be normal or can also be involved. Radiographs
of the guttural pouch are diagnostic of fluid or soft-
tissue infiltration of the pouch. Chondroids can be
visualised on radiographs occasionally, but they are
usually associated with some fluid accumulation that
can obscure their outline.
Management
Catheterisation of the guttural pouch and lavage is
indicated in the first instance. Great care must be
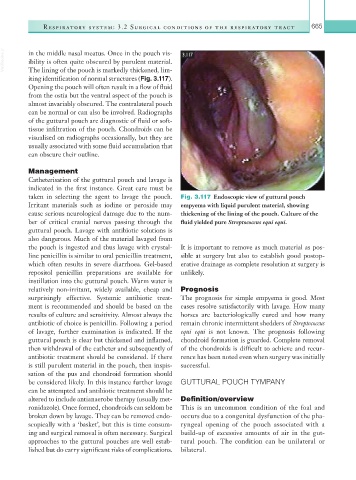
taken in selecting the agent to lavage the pouch. Fig. 3.117 Endoscopic view of guttural pouch
Irritant materials such as iodine or peroxide may empyema with liquid purulent material, showing
cause serious neurological damage due to the num- thickening of the lining of the pouch. Culture of the
ber of critical cranial nerves passing through the fluid yielded pure Streptococcus equi equi.
guttural pouch. Lavage with antibiotic solutions is
also dangerous. Much of the material lavaged from
the pouch is ingested and thus lavage with crystal- It is important to remove as much material as pos-
line penicillin is similar to oral penicillin treatment, sible at surgery but also to establish good postop-
which often results in severe diarrhoea. Gel-based erative drainage as complete resolution at surgery is
repositol penicillin preparations are available for unlikely.
instillation into the guttural pouch. Warm water is
relatively non-irritant, widely available, cheap and Prognosis
surprisingly effective. Systemic antibiotic treat- The prognosis for simple empyema is good. Most
ment is recommended and should be based on the cases resolve satisfactorily with lavage. How many
results of culture and sensitivity. Almost always the horses are bacteriologically cured and how many
antibiotic of choice is penicillin. Following a period remain chronic intermittent shedders of Streptococcus
of lavage, further examination is indicated. If the equi equi is not known. The prognosis following
guttural pouch is clear but thickened and inflamed, chondroid formation is guarded. Complete removal
then withdrawal of the catheter and subsequently of of the chondroids is difficult to achieve and recur-
antibiotic treatment should be considered. If there rence has been noted even when surgery was initially
is still purulent material in the pouch, then inspis- successful.
sation of the pus and chondroid formation should
be considered likely. In this instance further lavage GUTTURAL POUCH TYMPANY
can be attempted and antibiotic treatment should be
altered to include antianaerobe therapy (usually met- Definition/overview
ronidazole). Once formed, chondroids can seldom be This is an uncommon condition of the foal and
broken down by lavage. They can be removed endo- occurs due to a congenital dysfunction of the pha-
scopically with a ‘basket’, but this is time consum- ryngeal opening of the pouch associated with a
ing and surgical removal is often necessary. Surgical build-up of excessive amounts of air in the gut-
approaches to the guttural pouches are well estab- tural pouch. The condition can be unilateral or
lished but do carry significant risks of complications. bilateral.