Page 415 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 415
Diagnostic Imaging 381
VetBooks.ir
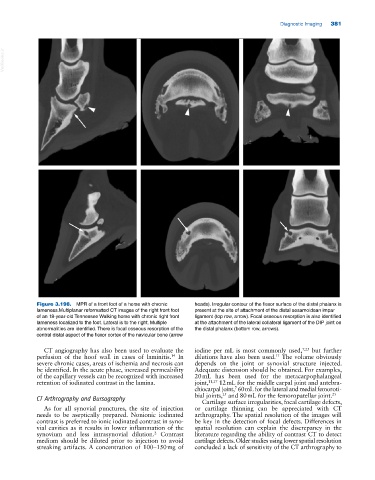
Figure 3.198. MPR of a front foot of a horse with chronic heads). Irregular contour of the flexor surface of the distal phalanx is
lameness.Multiplanar reformatted CT images of the right front foot present at the site of attachment of the distal sesamoidean impar
of an 18‐year‐old Tennessee Walking horse with chronic right front ligament (top row, arrow). Focal osseous resorption is also identified
lameness localized to the foot. Lateral is to the right. Multiple at the attachment of the lateral collateral ligament of the DIP joint on
abnormalities are identified. There is focal osseous resorption of the the distal phalanx (bottom row, arrows).
central distal aspect of the flexor cortex of the navicular bone (arrow
CT angiography has also been used to evaluate the iodine per mL is most commonly used, 7,25 but further
perfusion of the hoof wall in cases of laminitis. In dilutions have also been used. The volume obviously
11
14
severe chronic cases, areas of ischemia and necrosis can depends on the joint or synovial structure injected.
be identified. In the acute phase, increased permeability Adequate distension should be obtained. For examples,
of the capillary vessels can be recognized with increased 20 mL has been used for the metacarpophalangeal
retention of iodinated contrast in the lamina. joint, 11,17 12 mL for the middle carpal joint and antebra
chiocarpal joint, 60 mL for the lateral and medial femoroti
7
25
CT Arthrography and Bursography bial joints, and 80 mL for the femoropatellar joint. 25
Cartilage surface irregularities, focal cartilage defects,
As for all synovial punctures, the site of injection or cartilage thinning can be appreciated with CT
needs to be aseptically prepared. Nonionic iodinated arthrography. The spatial resolution of the images will
contrast is preferred to ionic iodinated contrast in syno be key in the detection of focal defects. Differences in
vial cavities as it results in lower inflammation of the spatial resolution can explain the discrepancy in the
synovium and less intrasynovial dilution. Contrast literature regarding the ability of contrast CT to detect
2
medium should be diluted prior to injection to avoid cartilage defects. Older studies using lower spatial resolution
streaking artifacts. A concentration of 100–150 mg of concluded a lack of sensitivity of the CT arthrography to