Page 165 - BSAVA Guide to Pain Management in Small Animal Practice
P. 165
BSAVA Guide to Pain Management in Small Animal Practice
VetBooks.ir may also be used in the management of veterinary species, despite their recogni ed
e cacy, the owners must be informed of the
cancer associated pain.
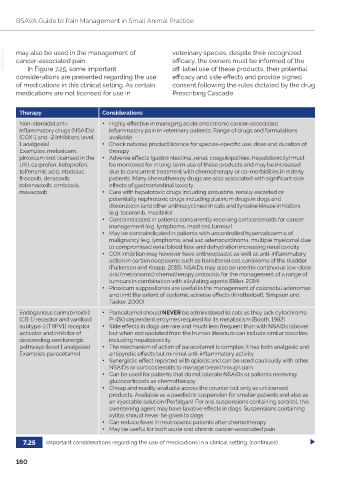
In igure . , some important
o label use of these products, their potential
considerations are presented regarding the use e cacy and side e ects and provide signed
of medications in this clinical setting. As certain consent following the rules dictated by the drug
medications are not licensed for use in Prescribing Cascade.
Therapy Considerations
Non steroidal anti • ighly e ective in managing acute and chronic cancer associated
in ammatory drugs NSAI s in ammatory pain in veterinary patients. Range of drugs and formulations
C 1 and inhibitors; level available
1 analgesia • Check national product licence for species speci c use, dose and duration of
Examples meloxicam, therapy
piroxicam not licensed in the • Adverse e ects gastrointestinal, renal, coagulopathies, hepatotoxicity must
U , carprofen, ketoprofen, be monitored for in long term use of these products and may be increased
tolfenamic acid, etodolac, due to concurrent treatment with chemotherapy or co morbidities in elderly
rocoxib, deracoxib, patients. any chemotherapy drugs are also associated with signi cant side
robenacoxib, cimicoxib, e ects of gastrointestinal toxicity
mavacoxib • Care with hepatotoxic drugs including lomustine, renally excreted or
potentially nephrotoxic drugs including platinum drugs in dogs and
doxorubicin and other anthracyclines in cats and tyrosine kinase inhibitors
e.g. toceranib, masitinib
• Contraindicated in patients concurrently receiving corticosteroids for cancer
management e.g. lymphoma, mast cell tumour
• ay be contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled hypercalcaemia of
malignancy e.g. lymphoma, anal sac adenocarcinoma, multiple myeloma due
to compromised renal blood ow and dehydration increasing renal toxicity
• C inhibition may however have antineoplastic as well as anti in ammatory
action in certain neoplasms such as transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder
ulkerson and napp, 1 . NSAI s may also be used in continuous low dose
oral metronomic chemotherapy protocols for the management of a range of
tumours in combination with alkylating agents Biller, 14
• Piroxicam suppositories are useful in the management of colorectal adenomas
and limit the extent of systemic adverse e ects nottenbelt, Simpson and
asker,
Endogenous cannabinoid 1 • Paracetamol should NEVER be administered to cats as they lack cytochrome
CB 1 receptor and vanilloid P 4 dependent en ymes re uired for its metabolism Booth, 198
subtype 1 RPV1 receptor • Side e ects in dogs are rare and much less fre uent than with NSAI s above
activator and inhibitor of but when extrapolated from the human literature can include similar toxicities
descending serotonergic including hepatotoxicity
pathways level 1 analgesia • he mechanism of action of paracetamol is complex; it has both analgesic and
Examples paracetamol antipyretic e ects but minimal anti in ammatory activity
• Synergistic e ect reported with opioids and can be used cautiously with other
NSAI s or corticosteroids to manage breakthrough pain
• Can be used for patients that do not tolerate NSAI s or patients receiving
glucocorticoids as chemotherapy
• Cheap and readily available across the counter but only as unlicensed
products. Available as a paediatric suspension for smaller patients and also as
an in ectable solution Perfalgan . or oral suspensions containing sorbitol, this
sweetening agent may have laxative e ects in dogs. Suspensions containing
xylitol should never be given to dogs
• Can reduce fever in neutropenic patients after chemotherapy
• ay be useful for both acute and chronic cancer associated pain
Important considerations regarding the use of medications in a clinical setting. continues
160
Ch7H Pain Management.indd 160 19/12/2018 10:46