Page 2375 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2375
Upper Gastrointestinal Radiographic Contrast Series 1173
VetBooks.ir
C
A B
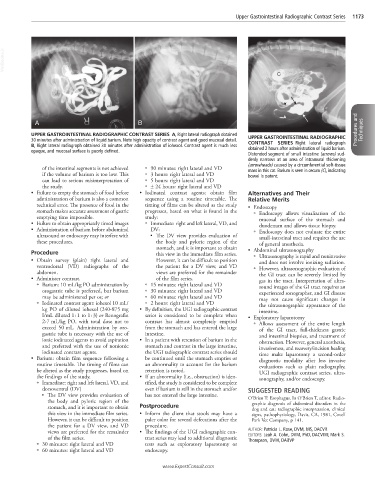
UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL RADIOGRAPHIC CONTRAST SERIES A, Right lateral radiograph obtained Procedures and Techniques
30 minutes after administration of liquid barium. Note high opacity of contrast agent and good mucosal detail. UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL RADIOGRAPHIC
B, Right lateral radiograph obtained 30 minutes after administration of iohexol. Contrast agent is much less CONTRAST SERIES Right lateral radiograph
opaque, and mucosal surface is poorly defined. obtained 2 hours after administration of liquid barium.
Distended segment of small intestine (arrows) sud-
denly narrows at an area of intramural thickening
(arrowheads) caused by a circumferential soft-tissue
of the intestinal segments is not achieved ○ 90 minutes: right lateral and VD mass in this cat. Barium is seen in cecum (C), indicating
if the volume of barium is too low. This ○ 3 hours: right lateral and VD bowel is patent.
can lead to serious misinterpretation of ○ 5 hours: right lateral and VD
the study. ○ ± 24 hours: right lateral and VD
• Failure to empty the stomach of food before • Iodinated contrast agents: obtain film Alternatives and Their
administration of barium is also a common sequence using a routine timetable. The Relative Merits
technical error. The presence of food in the timing of films can be altered as the study • Endoscopy
stomach makes accurate assessment of gastric progresses, based on what is found in the ○ Endoscopy allows visualization of the
emptying time impossible. study: mucosal surface of the stomach and
• Failure to obtain appropriately timed images ○ Immediate: right and left lateral, VD, and duodenum and allows tissue biopsy.
• Administration of barium before abdominal DV: ○ Endoscopy does not evaluate the entire
ultrasound or endoscopy may interfere with ■ The DV view provides evaluation of small-intestinal tract and requires the use
these procedures. the body and pyloric region of the of general anesthesia.
stomach, and it is important to obtain • Abdominal ultrasonography
Procedure this view in the immediate film series. ○ Ultrasonography is rapid and noninvasive
• Obtain survey (plain) right lateral and However, it can be difficult to position and does not involve ionizing radiation.
ventrodorsal (VD) radiographs of the the patient for a DV view, and VD ○ However, ultrasonographic evaluation of
abdomen. views are preferred for the remainder the GI tract can be severely limited by
• Administer contrast. of the film series. gas in the tract. Interpretation of ultra-
○ Barium: 10 mL/kg PO administration by ○ 15 minutes: right lateral and VD sound images of the GI tract requires an
orogastric tube is preferred, but barium ○ 30 minutes: right lateral and VD experienced sonographer, and GI disease
may be administered per os; or ○ 60 minutes: right lateral and VD may not cause significant changes in
○ Iodinated contrast agent: iohexol 10 mL/ ○ 2 hours: right lateral and VD the ultrasonographic appearance of the
kg PO of diluted iohexol (240-875 mg • By definition, the UGI radiographic contrast intestine.
I/mL diluted 1 : 1 to 1 : 3) or Renografin series is considered to be complete when • Exploratory laparotomy
2-7 mL/kg PO, with total dose not to contrast has almost completely emptied ○ Allows assessment of the entire length
exceed 50 mL. Administration by oro- from the stomach and has entered the large of the GI tract, full-thickness gastric
gastric tube is necessary with the use of intestine. and intestinal biopsies, and treatment of
ionic iodinated agents to avoid aspiration • In a patient with retention of barium in the obstruction. However, general anesthesia,
and preferred with the use of nonionic stomach and contrast in the large intestine, invasiveness, and recovery/incision healing
iodinated contrast agents. the UGI radiographic contrast series should time make laparotomy a second-order
• Barium: obtain film sequence following a be continued until the stomach empties or diagnostic modality after less invasive
routine timetable. The timing of films can an abnormality to account for the barium evaluations such as plain radiography,
be altered as the study progresses, based on retention is noted. UGI radiographic contrast series, ultra-
the findings of the study. • If an abnormality (i.e., obstruction) is iden- sonography, and/or endoscopy.
○ Immediate: right and left lateral, VD, and tified, the study is considered to be complete
dorsoventral (DV) even if barium is still in the stomach and/or SUGGESTED READING
The DV view provides evaluation of has not entered the large intestine.
■ O’Brien T: Esophagus. In O’Brien T, editor: Radio-
the body and pyloric region of the graphic diagnosis of abdominal disorders in the
stomach, and it is important to obtain Postprocedure dog and cat: radiographic interpretation, clinical
this view in the immediate film series. • Inform the client that stools may have a signs, pathophysiology, Davis, CA, 1981, Covell
However, it can be difficult to position paler color for several defecations after the Park Vet Company, p 141.
the patient for a DV view, and VD procedure.
views are preferred for the remainder • The findings of the UGI radiographic con- AUTHOR: Patricia L. Rose, DVM, MS, DACVR
EDITORS: Leah A. Cohn, DVM, PhD, DACVIM; Mark S.
of the film series. trast series may lead to additional diagnostic Thompson, DVM, DABVP
○ 30 minutes: right lateral and VD tests such as exploratory laparotomy or
○ 60 minutes: right lateral and VD endoscopy.
www.ExpertConsult.com