Page 2542 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2542
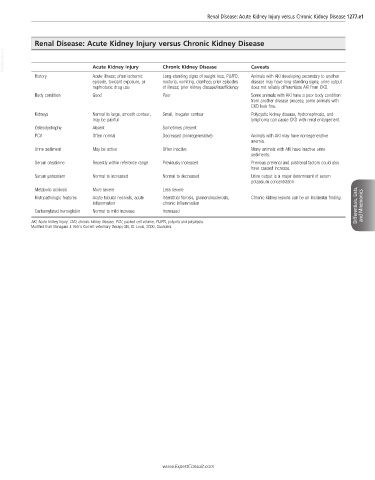
Renal Disease: Acute Kidney Injury versus Chronic Kidney Disease 1277.e1
Renal Disease: Acute Kidney Injury versus Chronic Kidney Disease
VetBooks.ir Acute Kidney Injury Chronic Kidney Disease Caveats
History Acute illness; often ischemic Long-standing signs of weight loss, PU/PD, Animals with AKI developing secondary to another
episode, toxicant exposure, or nocturia, vomiting, diarrhea; prior episodes disease may have long-standing signs; urine output
nephrotoxic drug use of illness; prior kidney disease/insufficiency does not reliably differentiate AKI from CKD.
Body condition Good Poor Some animals with AKI have a poor body condition
from another disease process; some animals with
CKD look fine.
Kidneys Normal to large, smooth contour, Small, irregular contour Polycystic kidney disease, hydronephrosis, and
may be painful lymphoma can cause CKD with renal enlargement.
Osteodystrophy Absent Sometimes present
PCV Often normal Decreased (nonregenerative) Animals with AKI may have nonregenerative
anemia.
Urine sediment May be active Often inactive Many animals with AKI have inactive urine
sediments.
Serum creatinine Recently within reference range Previously increased Previous prerenal and postrenal factors could also
have caused increase.
Serum potassium Normal to increased Normal to decreased Urine output is a major determinant of serum
potassium concentration.
Metabolic acidosis More severe Less severe
Histopathologic features Acute tubular necrosis, acute Interstitial fibrosis, glomerulosclerosis, Chronic kidney lesions can be an incidental finding.
inflammation chronic inflammation Differentials, Lists, and Mnemonics
Carbamylated hemoglobin Normal to mild increase Increased
AKI, Acute kidney injury; CKD, chronic kidney disease; PCV, packed cell volume; PU/PD, polyuria and polydipsia.
Modified from Bonagura J: Kirk’s Current veterinary therapy XIII, St. Louis, 2000, Saunders.
www.ExpertConsult.com