Page 2548 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2548
Shock Spinal Reflexes 1281.e1
Shock
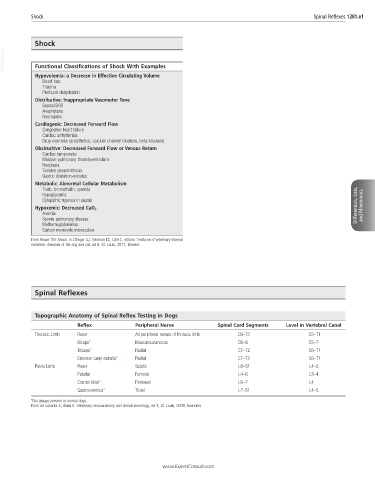
VetBooks.ir Functional Classifications of Shock With Examples
Hypovolemia: a Decrease in Effective Circulating Volume
Blood loss
Trauma
Profound dehydration
Distributive: Inappropriate Vasomotor Tone
Sepsis/SIRS
Anaphylaxis
Neurogenic
Cardiogenic: Decreased Forward Flow
Congestive heart failure
Cardiac arrhythmias
Drug overdose (anesthetics, calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers)
Obstructive: Decreased Forward Flow or Venous Return
Cardiac tamponade
Massive pulmonary thromboembolism
Neoplasia
Tension pneumothorax
Gastric dilatation-volvulus
Metabolic: Abnormal Cellular Metabolism
Toxic: bromethalin, cyanide
Hypoglycemia
Cytopathic hypoxia in sepsis
Hypoxemic: Decreased CaO 2 Differentials, Lists, and Mnemonics
Anemia
Severe pulmonary disease
Methemoglobinemia
Carbon monoxide intoxication
From Rieser TM: Shock. In Ettinger SJ, Feldman EC, Côté E, editors: Textbook of veterinary internal
medicine: diseases of the dog and cat, ed 8, St. Louis, 2017, Elsevier.
Spinal Reflexes
Topographic Anatomy of Spinal Reflex Testing in Dogs
Reflex Peripheral Nerve Spinal Cord Segments Level in Vertebral Canal
Thoracic Limb Flexor All peripheral nerves of thoracic limb C6–T2 C5–T1
Biceps* Musculocutaneous C6–8 C5–7
Triceps* Radial C7–T2 C6–T1
Extensor carpi radialis* Radial C7–T2 C6–T1
Pelvic Limb Flexor Sciatic L6–S1 L4–5
Patellar Femoral L4–6 L3–4
Cranial tibial* Peroneal L6–7 L4
Gastrocnemius* Tibial L7–S1 L4–5
*Not always present in normal dogs.
From de Lahunta A, Glass E: Veterinary neuroanatomy and clinical neurology, ed 3, St. Louis, 2009, Saunders.
www.ExpertConsult.com