Page 2558 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2558
1288 Toxicants, Radiopaque Tremors
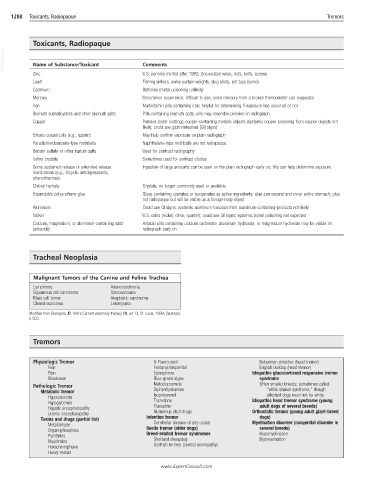
Toxicants, Radiopaque
VetBooks.ir Name of Substance/Toxicant Comments
Zinc U.S. pennies minted after 1982; zinc-coated wires, nuts, bolts, screws
Lead Fishing sinkers, some curtain weights, slug shots, pet toys (some)
Cadmium Batteries (metal poisoning unlikely)
Mercury Uncommon occurrence; difficult to see, since mercury from a broken thermometer can evaporate
Iron Multivitamin pills containing iron; helpful for determining if exposure has occurred or not
Bismuth subsalicylates and other bismuth salts Pills containing bismuth salts; pills may resemble pennies on radiograph.
Copper Pennies (outer coating); copper-containing metallic objects (systemic copper poisoning from copper objects not
likely; could see gastrointestinal [GI] signs)
Enteric-coated pills (e.g., aspirin) May help confirm exposure on plain radiograph
Paradichlorobenzene-type mothballs Naphthalene-type mothballs are not radiopaque.
Barium sulfate or other barium salts Used for contrast radiography
Iodine crystals Sometimes used for contrast studies
Some sustained-release or extended-release Ingestion of large amounts can be seen on the plain radiograph early on; this can help determine exposure.
medications (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants,
phenothiazines)
Chloral hydrate Crystals; no longer commonly used or available
Expandable polyurethane glue Glues containing cyanates or isocyanates as active ingredients; glue can expand and cover entire stomach; glue
not radiopaque but will be visible as a foreign-body object
Aluminum Could see GI signs; systemic aluminum toxicosis from aluminum-containing products not likely
Nickel U.S. coins (nickel, dime, quarter); could see GI signs; systemic nickel poisoning not expected
Calcium, magnesium, or aluminum-containing salts Antacid pills containing calcium carbonate, aluminum hydroxide, or magnesium hydroxide may be visible on
(antacids) radiograph early on.
Tracheal Neoplasia
Malignant Tumors of the Canine and Feline Trachea
Lymphoma Adenocarcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma Osteosarcoma
Mast cell tumor Anaplastic carcinoma
Chondrosarcoma Leiomyoma
Modified from Bonagura JD: Kirk’s Current veterinary therapy XIII, ed 13, St. Louis, 1999, Saunders,
p 503.
Tremors
Physiologic Tremor 5-Fluorouracil Doberman pinscher (head tremor)
Fear Fentanyl/droperidol English bulldog (head tremor)
Pain Epinephrine Idiopathic glucocorticoid responsive tremor
Weakness Blue-green algae syndrome
Pathologic Tremor Metoclopramide Often smaller breeds; sometimes called
Metabolic tremor Diphenhydramine “white shaker syndrome,” though
Hypocalcemia Isoproterenol affected dogs need not be white.
Hypoglycemia Trazodone Idiopathic head tremor syndrome (young
Hepatic encephalopathy Fluoxetine adult dogs of several breeds)
Uremic encephalopathy Numerous illicit drugs Orthostatic tremor (young adult giant-breed
Toxins and drugs (partial list) Intention tremor dogs)
Metaldehyde Cerebellar disease of any cause Myelination disorder (congenital disorder in
Organophosphate Senile tremor (older dogs) several breeds)
Pyrethrins Breed-related tremor syndromes Hypomyelination
Mycotoxins Shetland sheepdog Dysmyelination
Hexachlorophene Scottish terriers (central axonopathy)
Heavy metals
www.ExpertConsult.com