Page 2562 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2562
Urinary Tract Infections, Recurrent and Persistent Uroliths: Radiographic and Physical Appearance 1291
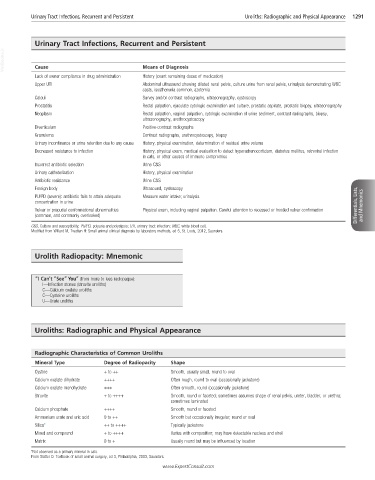
Urinary Tract Infections, Recurrent and Persistent
VetBooks.ir Cause Means of Diagnosis
Lack of owner compliance in drug administration History (count remaining doses of medication)
Upper UTI Abdominal ultrasound showing dilated renal pelvis, culture urine from renal pelvis, urinalysis demonstrating WBC
casts, isosthenuria common, azotemia
Calculi Survey and/or contrast radiographs, ultrasonography, cystoscopy
Prostatitis Rectal palpation, ejaculate cytologic examination and culture, prostatic aspirate, prostatic biopsy, ultrasonography
Neoplasm Rectal palpation, vaginal palpation, cytologic examination of urine sediment, contrast radiographs, biopsy,
ultrasonography, urethrocystoscopy
Diverticulum Positive-contrast radiographs
Granuloma Contrast radiographs, urethrocystoscopy, biopsy
Urinary incontinence or urine retention due to any cause History, physical examination, determination of residual urine volume
Decreased resistance to infection History, physical exam, medical evaluation to detect hyperadrenocorticism, diabetes mellitus, retroviral infection
in cats, or other causes of immune compromise
Incorrect antibiotic selection Urine C&S
Urinary catheterization History, physical examination
Antibiotic resistance Urine C&S
Foreign body Ultrasound, cystoscopy
PU/PD (severe): antibiotic fails to attain adequate Measure water intake; urinalysis
concentration in urine Differentials, Lists, and Mnemonics
Vulvar or preputial conformational abnormalities Physical exam, including vaginal palpation. Careful attention to recessed or hooded vulvar confirmation
(common, and commonly overlooked)
C&S, Culture and susceptibility; PU/PD, polyuria and polydipsia; UTI, urinary tract infection; WBC, white blood cell.
Modified from Willard M, Tvedten H: Small animal clinical diagnosis by laboratory methods, ed 5, St. Louis, 2012, Saunders.
Urolith Radiopacity: Mnemonic
“I Can’t “See” You” (from more to less radiopaque):
I—Infection stones (struvite uroliths)
C—Calcium oxalate uroliths
C—Cysteine uroliths
U—Urate uroliths
Uroliths: Radiographic and Physical Appearance
Radiographic Characteristics of Common Uroliths
Mineral Type Degree of Radiopacity Shape
Cystine + to ++ Smooth, usually small, round to oval
Calcium oxalate dihydrate ++++ Often rough, round to oval (occasionally jackstone)
Calcium oxalate monohydrate +++ Often smooth, round (occasionally jackstone)
Struvite + to ++++ Smooth, round or faceted; sometimes assumes shape of renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, or urethra;
sometimes laminated
Calcium phosphate ++++ Smooth, round or faceted
Ammonium urate and uric acid 0 to ++ Smooth but occasionally irregular; round or oval
Silica* ++ to ++++ Typically jackstone
Mixed and compound + to ++++ Varies with composition; may have detectable nucleus and shell
Matrix 0 to + Usually round but may be influenced by location
*Not observed as a primary mineral in cats.
From Slatter D: Textbook of small animal surgery, ed 3, Philadelphia, 2003, Saunders.
www.ExpertConsult.com