Page 2561 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2561
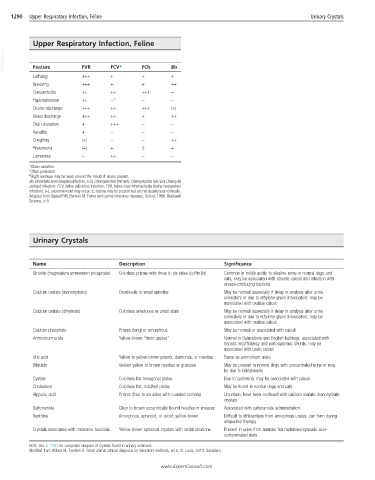
1290 Upper Respiratory Infection, Feline Urinary Crystals
Upper Respiratory Infection, Feline
VetBooks.ir Feature FVR FCV* FCh Bb
Lethargy +++ + + +
Sneezing +++ + + ++
Conjunctivitis ++ ++ +++ † −
Hypersalivation ++ − ‡ − −
Ocular discharge +++ ++ +++ (+)
Nasal discharge +++ ++ + ++
Oral ulceration + +++ − −
Keratitis + − − −
Coughing (+) − − ++
Pneumonia (+) + ± +
Lameness − ++ − −
*Strain variation.
† Often persistent.
‡ Slight wetness may be seen around the mouth if ulcers present.
Bb, Bordetella bronchiseptica infection; FCh, Chlamydia felis (formerly Chlamydophila felis and Chlamydia
psittaci) infection; FCV, feline calicivirus infection; FVR, feline viral rhinotracheitis (feline herpesvirus
infection); (+), uncommon but may occur; ±, lesions may be present but are not usually seen clinically.
Adapted from Gaskell RM, Bennett M: Feline and canine infectious diseases, Oxford, 1996, Blackwell
Science, p 8.
Urinary Crystals
Name Description Significance
Struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) Colorless prisms with three to six sides (coffin lid) Common in mildly acidic to alkaline urine in normal dogs and
cats; may be associated with struvite calculi and infection with
urease-producing bacteria
Calcium oxalate (monohydrate) Dumbbells or small spindles May be normal (especially if delay in analysis after urine
collection) or due to ethylene glycol intoxication; may be
associated with oxalate calculi
Calcium oxalate (dihydrate) Colorless envelopes or small stars May be normal (especially if delay in analysis after urine
collection) or due to ethylene glycol intoxication; may be
associated with oxalate calculi
Calcium phosphate Prisms (long) or amorphous May be normal or associated with calculi
Ammonium urate Yellow-brown “thorn apples” Normal in Dalmatians and English bulldogs; associated with
hepatic insufficiency and portosystemic shunts; may be
associated with urate calculi
Uric acid Yellow to yellow-brown prisms, diamonds, or rosettes Same as ammonium urate
Bilirubin Golden yellow to brown needles or granules May be present in normal dogs with concentrated urine or may
be due to bilirubinuria
Cystine Colorless flat hexagonal plates Due to cystinuria; may be associated with calculi
Cholesterol Colorless flat, notched plates May be found in normal dogs and cats
Hippuric acid Prisms (four to six sides with rounded corners) Uncertain; have been confused with calcium oxalate monohydrate
crystals
Sulfonamide Clear to brown eccentrically bound needles in sheaves Associated with sulfonamide administration
Xanthine Amorphous, spheroid, or ovoid; yellow-brown Difficult to differentiate from amorphous urates; can form during
allopurinol therapy
Crystals associated with melamine toxicosis Yellow-brown spherical crystals with radial striations Present in urine from animals fed melamine/cyanuric acid–
contaminated diets
NOTE: See p. 1131 for composite diagram of crystals found in urinary sediment.
Modified from Willard M, Tvedten H: Small animal clinical diagnosis by laboratory methods, ed 5, St. Louis, 2012, Saunders.
www.ExpertConsult.com