Page 2557 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 2557
Tonsillar Disorders 1287
(Continued from previous page)
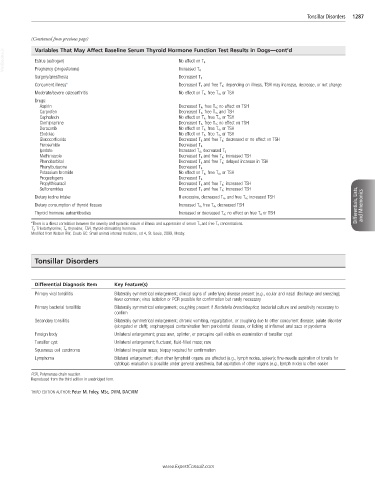
VetBooks.ir Variables That May Affect Baseline Serum Thyroid Hormone Function Test Results in Dogs—cont’d
Estrus (estrogen)
No effect on T 4
Pregnancy (progesterone)
Surgery/anesthesia Increased T 4
Decreased T 4
Concurrent illness* Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; depending on illness, TSH may increase, decrease, or not change
Moderate/severe osteoarthritis No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH
Drugs:
Aspirin Decreased T 4 , free T 4 ; no effect on TSH
Carprofen Decreased T 4 , free T 4 , and TSH
Cephalexin No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH
Clomipramine Decreased T 4 , free T 4 ; no effect on TSH
Deracoxib No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH
Etodolac No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH
Glucocorticoids Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; decreased or no effect on TSH
Furosemide Decreased T 4
Ipodate Increased T 4 , decreased T 3
Methimazole Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; increased TSH
Phenobarbital Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; delayed increase in TSH
Phenylbutazone Decreased T 4
Potassium bromide No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH
Progestogens Decreased T 4
Propylthiouracil Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; increased TSH
Sulfonamides Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; increased TSH
Dietary iodine intake If excessive, decreased T 4 , and free T 4 ; increased TSH
Dietary consumption of thyroid tissues Increased T 4 , free T 4 , decreased TSH Differentials, Lists, and Mnemonics
Thyroid hormone autoantibodies Increased or decreased T 4 ; no effect on free T 4 or TSH
*There is a direct correlation between the severity and systemic nature of illness and suppression of serum T 4 and free T 4 concentrations.
T 3 , Triiodothyronine; T 4 , thyroxine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Modified from Nelson RW, Couto GC: Small animal internal medicine, ed 4, St. Louis, 2009, Mosby.
Tonsillar Disorders
Differential Diagnosis Item Key Feature(s)
Primary viral tonsillitis Bilaterally symmetrical enlargement; clinical signs of underlying disease present (e.g., ocular and nasal discharge and sneezing);
fever common; virus isolation or PCR possible for confirmation but rarely necessary
Primary bacterial tonsillitis Bilaterally symmetrical enlargement; coughing present if Bordetella bronchiseptica; bacterial culture and sensitivity necessary to
confirm
Secondary tonsillitis Bilaterally symmetrical enlargement; chronic vomiting, regurgitation, or coughing due to other concurrent disease; palate disorder
(elongated or cleft); oropharyngeal contamination from periodontal disease, or licking at inflamed anal sacs or pyoderma
Foreign body Unilateral enlargement; grass awn, splinter, or porcupine quill visible on examination of tonsillar crypt
Tonsillar cyst Unilateral enlargement; fluctuant, fluid-filled mass; rare
Squamous cell carcinoma Unilateral irregular mass; biopsy required for confirmation
Lymphoma Bilateral enlargement; often other lymphoid organs are affected (e.g., lymph nodes, spleen); fine-needle aspiration of tonsils for
cytologic evaluation is possible under general anesthesia, but aspiration of other organs (e.g., lymph node) is often easier
PCR, Polymerase chain reaction.
Reproduced from the third edition in unabridged form.
THIRD EDITION AUTHOR: Peter M. Foley, MSc, DVM, DACVIM
www.ExpertConsult.com