Page 1050 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1050
1022 PART VIII Reproductive System Disorders
Pathognomonic changes occurring in the kidneys include
multifocal petechial hemorrhages, although this can be seen
VetBooks.ir with bacterial septicemia and associated thromboembolic
disorders as well. Intranuclear inclusion bodies can be dif-
ficult to find. Diagnosis by virus isolation or CHV-specific
PCR is confirmatory and desirable, especially before litter
mortality reaches 100%. Until recently, treatment of CHV
infection in neonates has been reported to be unrewarding
and rare, with recovery suspected to be associated with resid-
ual cardiac and neurologic damage. Treatment with immune
serum from affected dams is reported to be ineffective in
infected puppies. Successful treatment with the antiviral
agent acyclovir (Zovirax [Novopharm]) has been reported
(Davidson et al., 2003). Acyclovir is an antiviral agent with
activity against a variety of viruses including herpes simplex.
Acyclovir is preferentially taken up by susceptible viruses
and converted into the active triphosphate form, inhibiting
viral DNA replication. Acyclovir is poorly absorbed after
oral administration and is primarily hepatically metabolized.
Acyclovir can increase the toxicity of nephrotoxic drugs.
The half-life in humans is approximately 3 hours. Its use in
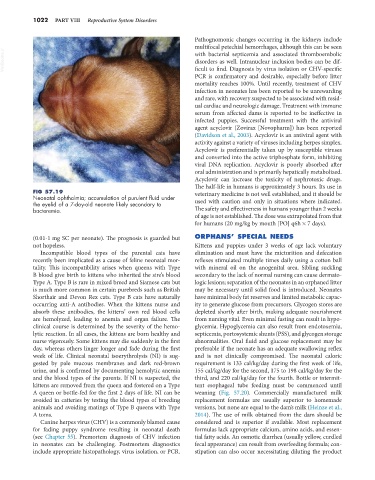
FIG 57.19 veterinary medicine is not well established, and it should be
Neonatal ophthalmia; accumulation of purulent fluid under used with caution and only in situations where indicated.
the eyelid of a 7-day-old neonate likely secondary to
bacteremia. The safety and effectiveness in humans younger than 2 weeks
of age is not established. The dose was extrapolated from that
for humans (20 mg/kg by mouth [PO] q6h × 7 days).
(0.01-1 mg SC per neonate). The prognosis is guarded but ORPHANS’ SPECIAL NEEDS
not hopeless. Kittens and puppies under 3 weeks of age lack voluntary
Incompatible blood types of the parental cats have elimination and must have the micturition and defecation
recently been implicated as a cause of feline neonatal mor- reflexes stimulated multiple times daily using a cotton ball
tality. This incompatibility arises when queens with Type with mineral oil on the anogenital area. Sibling suckling
B blood give birth to kittens who inherited the sire’s blood secondary to the lack of normal nursing can cause dermato-
Type A. Type B is rare in mixed breed and Siamese cats but logic lesions; separation of the neonates in an orphaned litter
is much more common in certain purebreds such as British may be necessary until solid food is introduced. Neonates
Shorthair and Devon Rex cats. Type B cats have naturally have minimal body fat reserves and limited metabolic capac-
occurring anti-A antibodies. When the kittens nurse and ity to generate glucose from precursors. Glycogen stores are
absorb these antibodies, the kittens’ own red blood cells depleted shortly after birth, making adequate nourishment
are hemolyzed, leading to anemia and organ failure. The from nursing vital. Even minimal fasting can result in hypo-
clinical course is determined by the severity of the hemo- glycemia. Hypoglycemia can also result from endotoxemia,
lytic reaction. In all cases, the kittens are born healthy and septicemia, portosystemic shunts (PSS), and glycogen storage
nurse vigorously. Some kittens may die suddenly in the first abnormalities. Oral fluid and glucose replacement may be
day, whereas others linger longer and fade during the first preferable if the neonate has an adequate swallowing reflex
week of life. Clinical neonatal isoerythrolysis (NI) is sug- and is not clinically compromised. The neonatal caloric
gested by pale mucous membranes and dark red-brown requirement is 133 cal/kg/day during the first week of life,
urine, and is confirmed by documenting hemolytic anemia 155 cal/kg/day for the second, 175 to 198 cal/kg/day for the
and the blood types of the parents. If NI is suspected, the third, and 220 cal/kg/day for the fourth. Bottle or intermit-
kittens are removed from the queen and fostered on a Type tent esophageal tube feeding must be commenced until
A queen or bottle-fed for the first 2 days of life. NI can be weaning (Fig. 57.20). Commercially manufactured milk
avoided in catteries by testing the blood types of breeding replacement formulas are usually superior to homemade
animals and avoiding matings of Type B queens with Type versions, but none are equal to the dam’s milk (Heinze et al.,
A toms. 2014). The use of milk obtained from the dam should be
Canine herpes virus (CHV) is a commonly blamed cause considered and is superior if available. Most replacement
for fading puppy syndrome resulting in neonatal death formulas lack appropriate calcium, amino acids, and essen-
(see Chapter 55). Premortem diagnosis of CHV infection tial fatty acids. An osmotic diarrhea (usually yellow, curdled
in neonates can be challenging. Postmortem diagnostics fecal appearance) can result from overfeeding formula; con-
include appropriate histopathology, virus isolation, or PCR. stipation can also occur necessitating diluting the product