Page 1415 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1415
VetBooks.ir
®
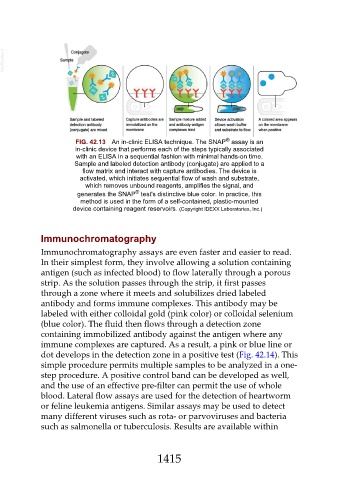
FIG. 42.13 An in-clinic ELISA technique. The SNAP assay is an
in-clinic device that performs each of the steps typically associated
with an ELISA in a sequential fashion with minimal hands-on time.
Sample and labeled detection antibody (conjugate) are applied to a
flow matrix and interact with capture antibodies. The device is
activated, which initiates sequential flow of wash and substrate,
which removes unbound reagents, amplifies the signal, and
®
generates the SNAP test's distinctive blue color. In practice, this
method is used in the form of a self-contained, plastic-mounted
device containing reagent reservoirs. (Copyright IDEXX Laboratories, Inc.)
Immunochromatography
Immunochromatography assays are even faster and easier to read.
In their simplest form, they involve allowing a solution containing
antigen (such as infected blood) to flow laterally through a porous
strip. As the solution passes through the strip, it first passes
through a zone where it meets and solubilizes dried labeled
antibody and forms immune complexes. This antibody may be
labeled with either colloidal gold (pink color) or colloidal selenium
(blue color). The fluid then flows through a detection zone
containing immobilized antibody against the antigen where any
immune complexes are captured. As a result, a pink or blue line or
dot develops in the detection zone in a positive test (Fig. 42.14). This
simple procedure permits multiple samples to be analyzed in a one-
step procedure. A positive control band can be developed as well,
and the use of an effective pre-filter can permit the use of whole
blood. Lateral flow assays are used for the detection of heartworm
or feline leukemia antigens. Similar assays may be used to detect
many different viruses such as rota- or parvoviruses and bacteria
such as salmonella or tuberculosis. Results are available within
1415