Page 274 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 274
Microbiology 243
the facilities required to perform these tests. ELISA kits ) is the most common approach for
16
In most countries, samples for virus isolation, the initial diagnosis of viral diseases (see also
especially in cases where a new or emerging dis- Chapter 6 and Table 4.5).
ease is suspected, are sent to specialist facilities
for a definitive diagnosis. National Reference Light microscope
Laboratories, Research Institutes and some
veterinary schools may also offer a set range of It is possible to see the elementary bodies of
virology services for a fee. In most regional or some viruses, in stained histological sections,
district laboratories, especially if molecular tools viewed with the ordinary light microscope. In
are not available, the use of serological screen- infected tissue sections, or prepared cell culture,
ing or antigen capture technology (for example, stained with haematoxylin and eosin there may
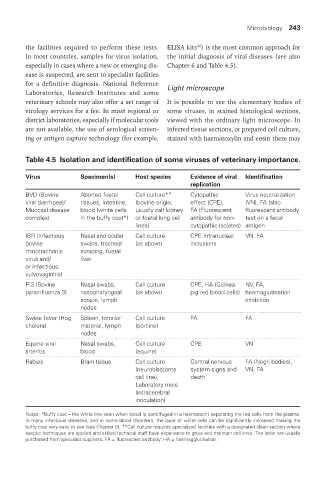
Table 4.5 Isolation and identification of some viruses of veterinary importance.
Virus Specimen(s) Host species Evidence of viral Identification
replication
BVD (Bovine Aborted foetal Cell culture** Cytopathic Virus neutralization
viral diarrhoea)/ tissues, intestine, (bovine origin, effect (CPE), (VN), FA (also
Mucosal disease blood (white cells usually calf kidney FA (Fluorescent fluorescent antibody
complex) in the buffy coat*) or foetal lung cell antibody for non- test on a fecal
lines) cytopathic isolates) antigen
IBR (Infectious Nasal and ocular Cell culture CPE Intranuclear VN, FA
bovine swabs, tracheal (as above) inclusions
rhinotracheitis scraping, foetal
virus and/ liver
or infectious
vulvovaginitis)
PI3 (Bovine Nasal swabs, Cell culture CPE, HA (Guinea NV, FA,
parainfluenza 3) nasopharyngeal (as above) pig red blood cells) heamaglutination
scrape, lymph inhibition
nodes
Swine fever (Hog Spleen, tonsilar Cell culture FA FA
cholera) material, lymph (porcine)
nodes
Equine viral Nasal swabs, Cell culture CPE VN
arteritis blood (equine)
Rabies Brain tissue Cell culture Central nervous FA (Negri bodies),
(neuroblastoma system signs and VN, FA
cell line), death
Laboratory mice
(intracerebral
inoculation)
Notes: *Buffy coat – the white line seen when blood is centrifuged in a haematocrit separating the red cells from the plasma.
In many infectious diseases, and in some blood disorders, the layer of white cells can be significantly increased making the
buffy coat very easy to see (see Chapter 5). **Cell culture requires specialized facilities with a designated clean section where
aseptic techniques are applied and skilled technical staff have experience to grow and maintain cell lines. The latter are usually
purchased from specialist suppliers. FA = fluorescent antibody; HA = haemagglutination.
Vet Lab.indb 243 26/03/2019 10:25