Page 440 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 440
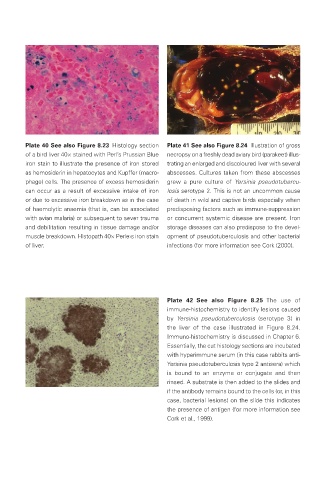
Plate 40 See also Figure 8.23 Histology section Plate 41 See also Figure 8.24 Illustration of gross
of a bird liver 40× stained with Perl’s Prussian Blue necropsy on a freshly dead aviary bird (parakeet) illus-
iron stain to illustrate the presence of iron stored trating an enlarged and discoloured liver with several
as hemosiderin in hepatocytes and Kupffer (macro- abscesses. Cultures taken from these abscesses
phage) cells. The presence of excess hemosiderin grew a pure culture of Yersinia pseudotubercu-
can occur as a result of excessive intake of iron losis serotype 2. This is not an uncommon cause
or due to excessive iron breakdown as in the case of death in wild and captive birds especially when
of haemolytic anaemia (that is, can be associated predisposing factors such as immune-suppression
with avian malaria) or subsequent to sever trauma or concurrent systemic disease are present. Iron
and debilitation resulting in tissue damage and/or storage diseases can also predispose to the devel-
muscle breakdown. Histopath 40× Perle›s iron stain opment of pseudotuberculosis and other bacterial
of liver. infections (for more information see Cork (2000).
Plate 42 See also Figure 8.25 The use of
immune-histochemistry to identify lesions caused
by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (serotype 3) in
the liver of the case illustrated in Figure 8.24.
Immuno-histochemistry is discussed in Chapter 6.
Essentially, the cut histology sections are incubated
with hyperimmune serum (in this case rabbits anti-
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis type 2 antisera) which
is bound to an enzyme or conjugate and then
rinsed. A substrate is then added to the slides and
if the antibody remains bound to the cells (or, in this
case, bacterial lesions) on the slide this indicates
the presence of antigen (for more information see
Cork et al., 1999).
Veterinary-plates.indd 23 26/03/2019 10:14