Page 338 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 338
304 Chapter 3
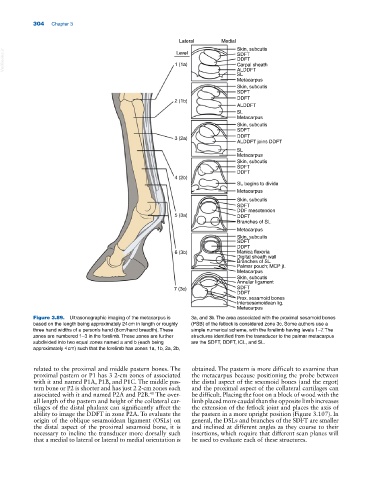
Lateral Medial Skin, subcutis
VetBooks.ir 1 (1a) SDFT
Level
DDFT
Carpal sheath
ALDDFT
SL
Metacarpus
Skin, subcutis
SDFT
DDFT
2 (1b)
ALDDFT
SL
Metacarpus
Skin, subcutis
SDFT
3 (2a) DDFT
ALDDFT joins DDFT
SL
Metacarpus
Skin, subcutis
SDFT
DDFT
4 (2b)
SL begins to divide
Metacarpus
Skin, subcutis
SDFT
DDF mesotendon
5 (3a) DDFT
Branches of SL
Metacarpus
Skin, subcutis
SDFT
DDFT
6 (3b) Manica flexoria
Digital sheath wall
Branches of SL
Palmar pouch; MCP jt.
Metacarpus
Skin, subcutis
Annular ligament
7 (3c) SDFT
DDFT
Prox. sesamoid bones
Intersesamoidean lig.
Metacarpus
Figure 3.89. Ultrasonographic imaging of the metacarpus is 3a, and 3b. The area associated with the proximal sesamoid bones
based on the length being approximately 24 cm in length or roughly (PSB) of the fetlock is considered zone 3c. Some authors use a
three hand widths of a person’s hand (8 cm/hand breadth). These simple numerical scheme, with the forelimb having levels 1–7. The
zones are numbered 1–3 in the forelimb. These zones are further structures identified from the transducer to the palmar metacarpus
subdivided into two equal zones named a and b (each being are the SDFT, DDFT, ICL, and SL.
approximately 4 cm) such that the forelimb has zones 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b,
related to the proximal and middle pastern bones. The obtained. The pastern is more difficult to examine than
proximal pastern or P1 has 3 2‐cm zones of associated the metacarpus because positioning the probe between
with it and named P1A, P1B, and P1C. The middle pas the distal aspect of the sesamoid bones (and the ergot)
tern bone or P2 is shorter and has just 2 2‐cm zones each and the proximal aspect of the collateral cartilages can
40
associated with it and named P2A and P2B. The over be difficult. Placing the foot on a block of wood with the
all length of the pastern and height of the collateral car limb placed more caudal than the opposite limb increases
tilages of the distal phalanx can significantly affect the the extension of the fetlock joint and places the axis of
ability to image the DDFT in zone P2A. To evaluate the the pastern in a more upright position (Figure 3.107). In
origin of the oblique sesamoidean ligament (OSLs) on general, the DSLs and branches of the SDFT are smaller
the distal aspect of the proximal sesamoid bone, it is and inclined at different angles as they course to their
necessary to incline the transducer more dorsally such insertions, which require that different scan planes will
that a medial to lateral or lateral to medial orientation is be used to evaluate each of these structures.