Page 443 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 443
428 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
blood in the peritubular capillaries. leave glomeruli (Fig. 23‐3). Efferent arteri-
oles from most glomeruli lead into capillary
Tubular secretion is the addition of sub-
VetBooks.ir stances to the tubular fluid by tubule cells. networks that surround tubules in the cor-
tex (peritubular capillaries). Efferents from
The secreted substances are produced in
the tubule cells (e.g., hydrogen ion and glomeruli deep in the cortex next to the
ammonia) or taken up by the tubule cells medulla contribute blood to vessels that
from the blood in the peritubular capillar- extend into the medulla. These vessels
ies (e.g., pharmaceuticals). Tubular reab- (vasa rectae) consist of straight descend-
sorption and secretion occur all along the ing branches (descending vasa rectae) that
nephron and collecting ducts in associa- empty into medullary capillaries, which are
tion with the peritubular capillaries. drained by straight ascending vessels
The renal microcirculation is unique in (ascending vasa rectae).
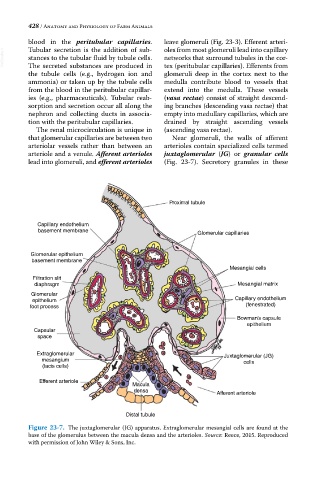
that glomerular capillaries are between two Near glomeruli, the walls of afferent
arteriolar vessels rather than between an arterioles contain specialized cells termed
arteriole and a venule. Afferent arterioles juxtaglomerular (JG) or granular cells
lead into glomeruli, and efferent arterioles (Fig. 23‐7). Secretory granules in these
Proximal tubule
Capillary endothelium
basement membrane Glomerular capillaries
Glomerular epithelium
basement membrane
Mesangial cells
Filtration slit
diaphragm Mesangial matrix
Glomerular
epithelium Capillary endothelium
foot process (fenestrated)
Bowman’s capsule
epithelium
Capsular
space
Extraglomerular Juxtaglomerular (JG)
mesangium cells
(lacis cells)
Efferent arteriole
Macula
densa Afferent arteriole
Distal tubule
Figure 23-7. The juxtaglomerular (JG) apparatus. Extraglomerular mesangial cells are found at the
base of the glomerulus between the macula densa and the arterioles. Source: Reece, 2015. Reproduced
with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.