Page 442 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 442
The Urinary System / 427
bases, and increases in blood levels of urea location in the kidney, and function. These
and creatinine.
VetBooks.ir of thousands to millions of similar micro- segments are named the proximal (convo-
luted) tubule, loop of Henle, and distal
Kidneys are composite organs that consist
(convoluted) tubule (Fig. 23‐3). The distal
scopic functional units, the nephrons. tubules of numerous nephrons connect to
Nephrons in all mammalian kidneys are sim- another tubular structure found in the kidney,
ilar in basic structure and function, but the the collecting duct (tubule). Collecting ducts
number of nephrons differs among mam- begin in the renal cortex, where they connect
mals. Large animals have more nephrons per with distal tubules, and extend into and
kidney than small animals (e.g., 4 million for through the renal medulla (Fig. 23‐3).
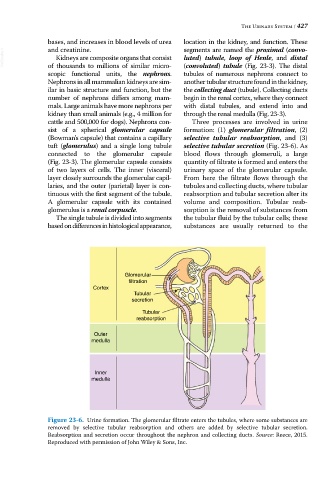
cattle and 500,000 for dogs). Nephrons con- Three processes are involved in urine
sist of a spherical glomerular capsule formation: (1) glomerular filtration, (2)
(Bowman’s capsule) that contains a capillary selective tubular reabsorption, and (3)
tuft (glomerulus) and a single long tubule selective tubular secretion (Fig. 23‐6). As
connected to the glomerular capsule blood flows through glomeruli, a large
(Fig. 23‐3). The glomerular capsule consists quantity of filtrate is formed and enters the
of two layers of cells. The inner (visceral) urinary space of the glomerular capsule.
layer closely surrounds the glomerular capil- From here the filtrate flows through the
laries, and the outer (parietal) layer is con- tubules and collecting ducts, where tubular
tinuous with the first segment of the tubule. reabsorption and tubular secretion alter its
A glomerular capsule with its contained volume and composition. Tubular reab-
glomerulus is a renal corpuscle. sorption is the removal of substances from
The single tubule is divided into segments the tubular fluid by the tubular cells; these
based on differences in histological appearance, substances are usually returned to the
Glomerular
filtration
Cortex
Tubular
secretion
Tubular
reabsorption
Outer
medulla
Inner
medulla
Figure 23-6. Urine formation. The glomerular filtrate enters the tubules, where some substances are
removed by selective tubular reabsorption and others are added by selective tubular secretion.
Reabsorption and secretion occur throughout the nephron and collecting ducts. Source: Reece, 2015.
Reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.