Page 513 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 513
29.7 Additional maging echniiues 525
(a) (c)
(b) (d)
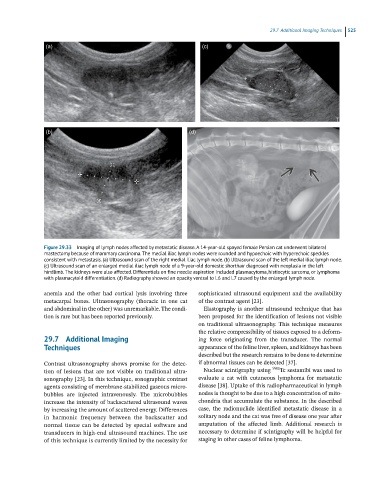
Figure 29.33 Imaging of lymph nodes affected by metastatic disease. A 14-year-old spayed female Persian cat underwent bilateral
mastectomy because of mammary carcinoma. The medial iliac lymph nodes were rounded and hypoechoic with hyperechoic speckles
consistent with metastasis. (a) Ultrasound scan of the right medial iliac lymph node. (b) Ultrasound scan of the left medial iliac lymph node.
(c) Ultrasound scan of an enlarged medial iliac lymph node of a 9-year-old domestic shorthair diagnosed with neoplasia in the left
hindlimb. The kidneys were also affected. Differentials on fine needle aspiration included plasmacytoma, histiocytic sarcoma, or lymphoma
with plasmacytoid differentiation. (d) Radiography showed an opacity ventral to L6 and L7 caused by the enlarged lymph node.
anemia and the other had cortical lysis involving three sophisticated ultrasound equipment and the availability
metacarpal bones. Ultrasonography (thoracic in one cat of the contrast agent [23].
and abdominal in the other) was unremarkable. The condi- Elastography is another ultrasound technique that has
tion is rare but has been reported previously. been proposed for the identification of lesions not visible
on traditional ultrasonography. This technique measures
the relative compressibility of tissues exposed to a deform-
29.7 Additional Imaging ing force originating from the transducer. The normal
Techniques appearance of the feline liver, spleen, and kidneys has been
described but the research remains to be done to determine
Contrast ultrasonography shows promise for the detec- if abnormal tissues can be detected [37].
tion of lesions that are not visible on traditional ultra- Nuclear scintigraphy using 99m Tc sestamibi was used to
sonography [23]. In this technique, sonographic contrast evaluate a cat with cutaneous lymphoma for metastatic
agents consisting of membrane‐stabilized gaseous micro- disease [38]. Uptake of this radiopharmaceutical in lymph
bubbles are injected intravenously. The microbubbles nodes is thought to be due to a high concentration of mito-
increase the intensity of backscattered ultrasound waves chondria that accumulate the substance. In the described
by increasing the amount of scattered energy. Differences case, the radionuclide identified metastatic disease in a
in harmonic frequency between the backscatter and solitary node and the cat was free of disease one year after
normal tissue can be detected by special software and amputation of the affected limb. Additional research is
transducers in high‐end ultrasound machines. The use necessary to determine if scintigraphy will be helpful for
of this technique is currently limited by the necessity for staging in other cases of feline lymphoma.