Page 511 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 511
29.5 DesheMeshees of Thef mphehea 523
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
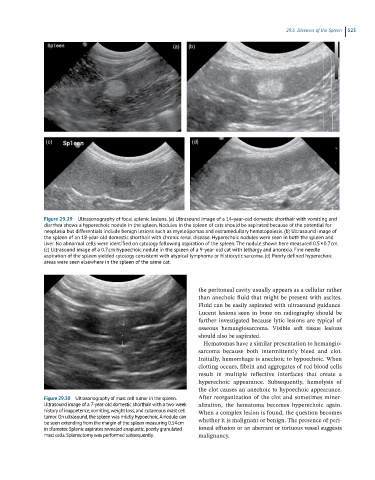
Figure 29.29 Ultrasonography of focal splenic lesions. (a) Ultrasound image of a 14-year-old domestic shorthair with vomiting and
diarrhea shows a hyperechoic nodule in the spleen. Nodules in the spleen of cats should be aspirated because of the potential for
neoplasia but differentials include benign lesions such as myelolipomas and extramedullary hematopoiesis. (b) Ultrasound image of
the spleen of an 18-year-old domestic shorthair with chronic renal disease. Hyperechoic nodules were seen in both the spleen and
liver. No abnormal cells were identified on cytology following aspiration of the spleen. The nodule shown here measured 0.5 × 0.7 cm.
(c) Ultrasound image of a 0.7 cm hypoechoic nodule in the spleen of a 9-year-old cat with lethargy and anorexia. Fine needle
aspiration of the spleen yielded cytology consistent with atypical lymphoma or histiocytic sarcoma. (d) Poorly defined hyperechoic
areas were seen elsewhere in the spleen of the same cat.
the peritoneal cavity usually appears as a cellular rather
than anechoic fluid that might be present with ascites.
Fluid can be easily aspirated with ultrasound guidance.
Lucent lesions seen in bone on radiography should be
further investigated because lytic lesions are typical of
osseous hemangiosarcoma. Visible soft tissue lesions
should also be aspirated.
Hematomas have a similar presentation to hemangio -
sarcoma because both intermittently bleed and clot.
Initially, hemorrhage is anechoic to hypoechoic. When
clotting occurs, fibrin and aggregates of red blood cells
result in multiple reflective interfaces that create a
hyperechoic appearance. Subsequently, hemolysis of
the clot causes an anechoic to hypoechoic appearance.
Figure 29.30 Ultrasonography of mast cell tumor in the spleen. After reorganization of the clot and sometimes miner -
Ultrasound image of a 7-year-old domestic shorthair with a two-week alization, the hematoma becomes hyperechoic again.
history of inappetence, vomiting, weight loss, and cutaneous mast cell When a complex lesion is found, the question becomes
tumor. On ultrasound, the spleen was mildly hypoechoic. A nodule can
be seen extending from the margin of the spleen measuring 0.54 cm whether it is malignant or benign. The presence of peri-
in diameter. Splenic aspirates revealed anaplastic, poorly granulated toneal effusion or an aberrant or tortuous vessel suggests
mast cells. Splenectomy was performed subsequently. malignancy.