Page 506 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 506
518 29 Hemolymphatic System
(a) (b) (c)
(d) (e) (f)
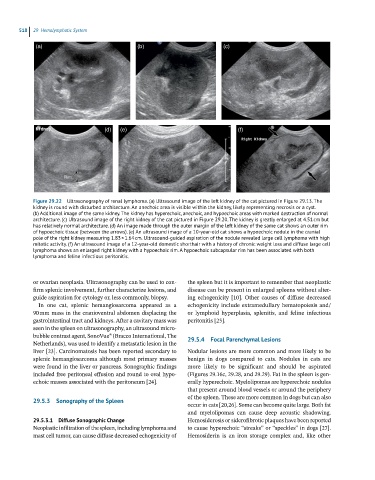
Figure 29.22 Ultrasonography of renal lymphoma. (a) Ultrasound image of the left kidney of the cat pictured in Figure 29.13. The
kidney is round with disturbed architecture. An anechoic area is visible within the kidney, likely representing necrosis or a cyst.
(b) Additional image of the same kidney. The kidney has hyperechoic, anechoic, and hypoechoic areas with marked destruction of normal
architecture. (c) Ultrasound image of the right kidney of the cat pictured in Figure 29.20. The kidney is greatly enlarged at 4.51 cm but
has relatively normal architecture. (d) An image made through the outer margin of the left kidney of the same cat shows an outer rim
of hypoechoic tissue (between the arrows). (e) An ultrasound image of a 10-year-old cat shows a hypoechoic nodule in the cranial
pole of the right kidney measuring 1.83 × 1.64 cm. Ultrasound-guided aspiration of the nodule revealed large cell lymphoma with high
mitotic activity. (f) An ultrasound image of a 12-year-old domestic shorthair with a history of chronic weight loss and diffuse large cell
lymphoma shows an enlarged right kidney with a hypoechoic rim. A hypoechoic subcapsular rim has been associated with both
lymphoma and feline infectious peritonitis.
or ovarian neoplasia. Ultrasonography can be used to con- the spleen but it is important to remember that neoplastic
firm splenic involvement, further characterize lesions, and disease can be present in enlarged spleens without alter-
guide aspiration for cytology or, less commonly, biopsy. ing echogenicity [10]. Other causes of diffuse decreased
In one cat, splenic hemangiosarcoma appeared as a echogenicity include extramedullary hematopoiesis and/
90 mm mass in the cranioventral abdomen displacing the or lymphoid hyperplasia, splenitis, and feline infectious
gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. After a cavitary mass was peritonitis [25].
seen in the spleen on ultrasonography, an ultrasound micro-
bubble contrast agent, SonoVue® (Bracco International, The 29.5.4 Focal Parenchymal Lesions
Netherlands), was used to identify a metastatic lesion in the
liver [23]. Carcinomatosis has been reported secondary to Nodular lesions are more common and more likely to be
splenic hemangiosarcoma although most primary masses benign in dogs compared to cats. Nodules in cats are
were found in the liver or pancreas. Sonographic findings more likely to be significant and should be aspirated
included free peritoneal effusion and round to oval hypo- (Figures 29.16c, 29.28, and 29.29). Fat in the spleen is gen-
echoic masses associated with the peritoneum [24]. erally hyperechoic. Myelolipomas are hyperechoic nodules
that present around blood vessels or around the periphery
of the spleen. These are more common in dogs but can also
29.5.3 Sonography of the Spleen
occur in cats [20,26]. Some can become quite large. Both fat
and myelolipomas can cause deep acoustic shadowing.
29.5.3.1 Diffuse Sonographic Change Hemosiderosis or siderofibrotic plaques have been reported
Neoplastic infiltration of the spleen, including lymphoma and to cause hyperechoic “streaks” or “speckles” in dogs [27].
mast cell tumor, can cause diffuse decreased echogenicity of Hemosiderin is an iron storage complex and, like other