Page 503 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 503
29.5 DesheMeshees of Thef mphehea 515
(a) (b)
(c)
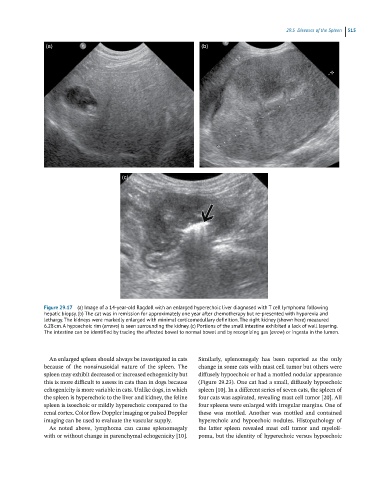
Figure 29.17 (a) Image of a 14-year-old Ragdoll with an enlarged hyperechoic liver diagnosed with T cell lymphoma following
hepatic biopsy. (b) The cat was in remission for approximately one year after chemotherapy but re-presented with hyporexia and
lethargy. The kidneys were markedly enlarged with minimal corticomedullary definition. The right kidney (shown here) measured
6.28 cm. A hypoechoic rim (arrows) is seen surrounding the kidney. (c) Portions of the small intestine exhibited a lack of wall layering.
The intestine can be identified by tracing the affected bowel to normal bowel and by recognizing gas (arrow) or ingesta in the lumen.
An enlarged spleen should always be investigated in cats Similarly, splenomegaly has been reported as the only
because of the nonsinusoidal nature of the spleen. The change in some cats with mast cell tumor but others were
spleen may exhibit decreased or increased echogenicity but diffusely hypoechoic or had a mottled nodular appearance
this is more difficult to assess in cats than in dogs because (Figure 29.23). One cat had a small, diffusely hypoechoic
echogenicity is more variable in cats. Unlike dogs, in which spleen [10]. In a different series of seven cats, the spleen of
the spleen is hyperechoic to the liver and kidney, the feline four cats was aspirated, revealing mast cell tumor [20]. All
spleen is isoechoic or mildly hyperechoic compared to the four spleens were enlarged with irregular margins. One of
renal cortex. Color flow Doppler imaging or pulsed Doppler these was mottled. Another was mottled and contained
imaging can be used to evaluate the vascular supply. hyperechoic and hypoechoic nodules. Histopathology of
As noted above, lymphoma can cause splenomegaly the latter spleen revealed mast cell tumor and myeloli-
with or without change in parenchymal echogenicity [10]. poma, but the identity of hyperechoic versus hypoechoic