Page 589 - Divyank Tyagi
P. 589
|
Understanding rooF Modeling Methods 555
Understanding Roof Modeling Methods
Certification In today’s construction environment, roofs come in a great number of shapes and sizes. They
Objective can be as simple as a pitched shed roof or can involve complex double-curved surfaces or
intersecting vaults. Once you understand the fundamental concepts, tools, and logic pertaining
to roofs, you will be able to design almost any roof shape.
Roofs are similar to floors and ceilings because they are sketch-based elements and can be
defined in generic types or with specific material assemblies. You can also change a roof element
from one type to another in the same manner as you can a floor or ceiling. A fundamental
difference between floors and roofs is that a roof’s thickness is generated above its referencing
level, not below. You can also easily create slopes in roofs by defining slopes in the roof’s sketch
lines.
In general, roofs can be constructed in four different ways:
◆ ◆ By footprint
◆ ◆ By extrusion
◆ ◆ By face
◆ ◆ Modeled in place
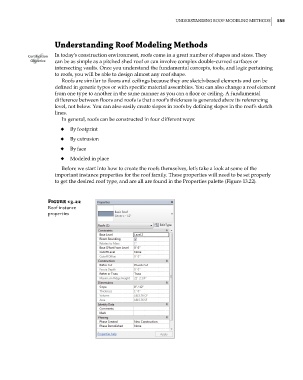
Before we start into how to create the roofs themselves, let’s take a look at some of the
important instance properties for the roof family. These properties will need to be set properly
to get the desired roof type, and are all are found in the Properties palette (Figure 13.22).
Figure 13.22
roof instance
properties
c13.indd 555 05-05-2014 16:57:15