Page 169 - C:\Users\Adik\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Marketer PPT LR\
P. 169
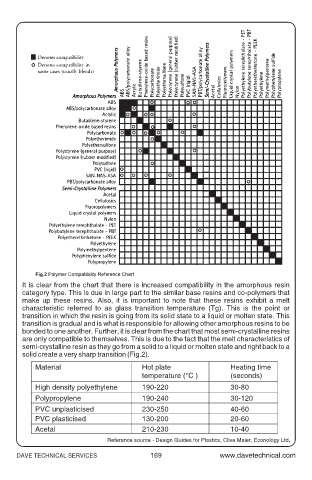
It is clear from the chart that there is increased compatibility in the amorphous resin
category type. This is due in large part to the similar base resins and co-polymers that
make up these resins. Also, it is important to note that these resins exhibit a melt
characteristic referred to as glass transition temperature (Tg). This is the point or
transition in which the resin is going from its solid state to a liquid or molten state. This
transition is gradual and is what is responsible for allowing other amorphous resins to be
bonded to one another. Further, it is clear from the chart that most semi-crystalline resins
are only compatible to themselves. This is due to the fact that the melt characteristics of
semi-crystalline resin as they go from a solid to a liquid or molten state and right back to a
solid create a very sharp transition (Fig.2).
Material Hot plate Heating time
temperature (°C ) (seconds)
High density polyethylene 190-220 30-80
Polypropylene 190-240 30-120
PVC unplasticised 230-250 40-60
PVC plasticised 130-200 20-60
Acetal 210-230 10-40
Referance source - Design Guides for Plastics, Clive Maier, Econology Ltd,
DAVE TECHNICAL SERVICES 169