Page 171 - C:\Users\Adik\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Marketer PPT LR\
P. 171
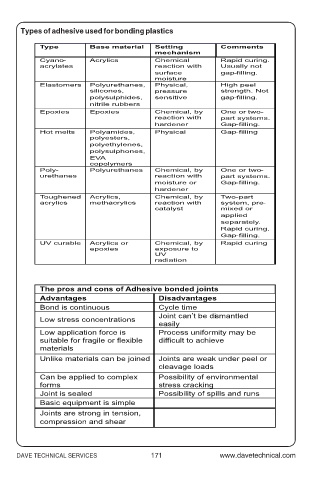
Types of adhesive used for bonding plastics
Type Base material Setting Comments
mechanism
Cyano- Acrylics Chemical Rapid curing.
acrylates reaction with Usually not
surface gap-filling.
moisture
Elastomers Polyurethanes, Physical, High peel
silicones, pressure strength. Not
polysulphides, sensitive gap-filling.
nitrile rubbers
Epoxies Epoxies Chemical, by One or two-
reaction with part systems.
hardener Gap-filling.
Hot melts Polyamides, Physical Gap-filling
polyesters,
polyethylenes,
polysulphones,
EVA
copolymers
Poly- Polyurethanes Chemical, by One or two-
urethanes reaction with part systems.
moisture or Gap-filling.
hardener
Toughened Acrylics, Chemical, by Two-part
acrylics methacrylics reaction with system, pre-
catalyst mixed or
applied
separately.
Rapid curing.
Gap-filling.
UV curable Acrylics or Chemical, by Rapid curing
epoxies exposure to
UV
radiation
The pros and cons of Adhesive bonded joints
Advantages Disadvantages
Bond is continuous Cycle time
Joint can’t be dismantled
Low stress concentrations easily
Low application force is Process uniformity may be
suitable for fragile or flexible difficult to achieve
materials
Unlike materials can be joined Joints are weak under peel or
cleavage loads
Can be applied to complex Possibility of environmental
forms stress cracking
Joint is sealed Possibility of spills and runs
Basic equipment is simple
Joints are strong in tension,
compression and shear
DAVE TECHNICAL SERVICES 171