Page 71 - C:\Users\Adik\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Marketer PPT LR\
P. 71
EXTRUDERS IN PLASTIC MACHINERY:
UNDERSTANDING FEED SCREWS & BARRELS
Extruder is a heart of Blow, Injection and Extrusion Machineries. Screw and Barrel
are the main component of Extruder. The screw housed by barrel is connected to a
drive which rotates it within barrel. The prime and basic responsibility of feed-screws
is of conveying and mixing the resins through the barrel chamber in a steady and
predictable manner.
The raw material enters through the feed throat and comes into contact with the
screw. The rotating screw forces the plastic pellets forward into the barrel. The barrel
is equipped with heaters which heat the material to melt. The heating profile for
barrel is set and heat is controlled through PID controllers increasing the
temperature of the barrel from the rear to the front. The material inside barrel gets
melted due to heat and frictional heat created between the solid bed and the extruder
barrel giving homogeneous melt at end of the screw.
Two types of mixing occur in the extruder:
Dispersive mixing, which breaks up agglomerated particles into the smallest
particle size, requires high energy and shear stress.
Distributive mixing, which uniformly distributes ingredients throughout the
mixture, requires less energy. Different types of extruders and screw designs have
different mixing ability.
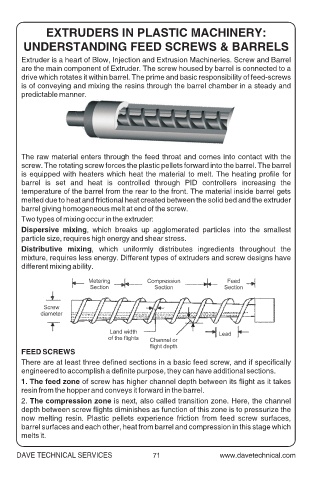
FEED SCREWS
There are at least three defined sections in a basic feed screw, and if specifically
engineered to accomplish a definite purpose, they can have additional sections.
1. The feed zone of screw has higher channel depth between its flight as it takes
resin from the hopper and conveys it forward in the barrel.
2. The compression zone is next, also called transition zone. Here, the channel
depth between screw flights diminishes as function of this zone is to pressurize the
now melting resin. Plastic pellets experience friction from feed screw surfaces,
barrel surfaces and each other, heat from barrel and compression in this stage which
melts it.
DAVE TECHNICAL SERVICES 71