Page 90 - C:\Users\Adik\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Marketer PPT LR\
P. 90
INJECTION MOULDING
Injection moulding is a process of forming an article by forcing molten plastic
material under pressure into a mould where it is cooled, solidified and
subsequently released by opening the two halves of the mould.
Injection moulding produces high-quality parts with consistent wall thickness and
dimensional accuracy, often used in mass-production and prototyping. The process
is capable of producing an infinite variety of part designs containing an equally
infinite variety of details such as threads, springs and hinges, and all in a single
moulding operation.
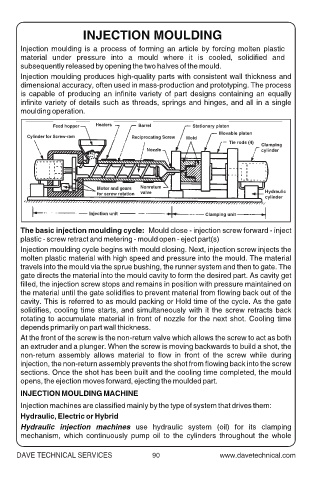
Feed hopper Heaters Barrel Stationary platen
Movable platen
Cylinder for Screw-ram Reciprocating Screw Mold
Tie rods (4)
Clamping
Nozzle cylinder
Motor and gears Nonretum
for screw rotation valve Hydraulic
cylinder
Injection unit Clamping unit
The basic injection moulding cycle: Mould close - injection screw forward - inject
plastic - screw retract and metering - mould open - eject part(s)
Injection moulding cycle begins with mould closing. Next, injection screw injects the
molten plastic material with high speed and pressure into the mould. The material
travels into the mould via the sprue bushing, the runner system and then to gate. The
gate directs the material into the mould cavity to form the desired part. As cavity get
filled, the injection screw stops and remains in position with pressure maintained on
the material until the gate solidifies to prevent material from flowing back out of the
cavity. This is referred to as mould packing or Hold time of the cycle. As the gate
solidifies, cooling time starts, and simultaneously with it the screw retracts back
rotating to accumulate material in front of nozzle for the next shot. Cooling time
depends primarily on part wall thickness.
At the front of the screw is the non-return valve which allows the screw to act as both
an extruder and a plunger. When the screw is moving backwards to build a shot, the
non-return assembly allows material to flow in front of the screw while during
injection, the non-return assembly prevents the shot from flowing back into the screw
sections. Once the shot has been built and the cooling time completed, the mould
opens, the ejection moves forward, ejecting the moulded part.
INJECTION MOULDING MACHINE
Injection machines are classified mainly by the type of system that drives them:
Hydraulic, Electric or Hybrid
Hydraulic injection machines use hydraulic system (oil) for its clamping
mechanism, which continuously pump oil to the cylinders throughout the whole
DAVE TECHNICAL SERVICES 90