Page 96 - C:\Users\Adik\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Marketer PPT LR\
P. 96
Rapid injection moulding:
Rapid Injection Moulding allows us to make prototype injection moulded parts in a
production thermoplastic resin in 2-5 weeks. These parts may be used for full
functional and fit testing as well as test marketing. Also called Prototype or Short-Run
Injection Moulding
Micro - Injection Mouldings:
This consists of obtaining injection moulded micro-parts that weigh less than one
tenth of a gram. It similarly covers the technique for obtaining large parts, but with
micro-shaping applications very high-precision is involved in both tooling as well as
production. The production is very precise with stringent part tolerances and
properties mostly working with difficult engineering materials.
Micro moulding products finds applications in high-technology systems, mainly in
sectors, such as biomedicine, consumer electronics, microelectronics and
micromechanics, car manufacturing, aeronautics and the aerospace industry.
Injection Compression Moulding (ICM)
ICM is an injection moulding technique where the melted polymer is injected into a
partially open mould. The mould closes compresses and distributes the melt
throughout the cavity, thus completing the filling and packing stage. Compression
can be either simultaneous with, or sequential to injection of polymer. ICM requires
modification of existing equipment or selection of the ICM option on new machines.
Equipment requirements include precise clamp positioning, accurate shot size
control on injection and speed control of the secondary clamp or compression
action. The process works on significantly lower injection pressure providing lower
moulded-in stress and thin walled part production.
Thermosets Injection Moulding: The Injection Moulding of Thermosets is similar to
the injection moulding of thermoplastics, except the material is kept cool until it is
pushed into the heated mould where it is cross-linked. The mould is then opened and
the hot, but rigid part is removed.
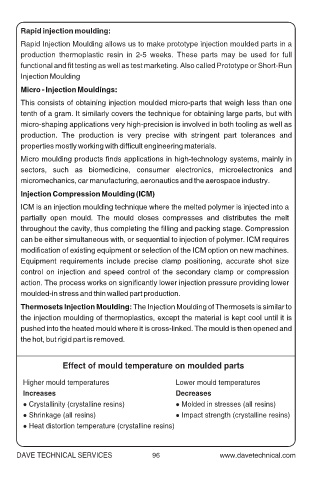
Effect of mould temperature on moulded parts
Higher mould temperatures Lower mould temperatures
Increases Decreases
l Crystallinity (crystalline resins) l Molded in stresses (all resins)
l Shrinkage (all resins) l Impact strength (crystalline resins)
l Heat distortion temperature (crystalline resins)
DAVE TECHNICAL SERVICES 96