Page 100 - C:\Users\Adik\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Marketer PPT LR\
P. 100
INJECTION MOULDS:
The mould determines the part's shape, conducts the hot plasticized material from
heating cylinder to the cavity, vents the entrapped air or gas, acts as a heat sink to
cool the part and finally, ejects the finished part without leaving marks or causing
damage. Moulds are made of special moulding steel, beryllium copper, stainless
steel, aluminum, brass, and kirksite. The finished mould surfaces are often polished
and coated to resist wear and aid in part ejection. Moulds are manufactured by
machining, EDM, or casting. The mould design, construction, the craftsmanship
largely determine the quality of the part and its manufacturing cost.
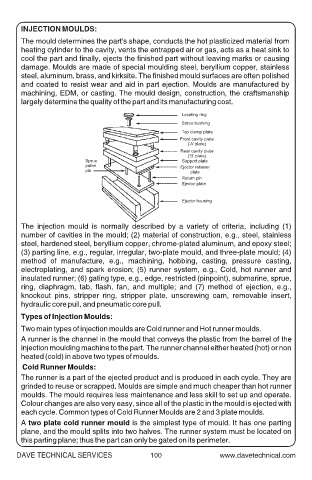
Locating ring
Sprue bushing
Top clamp plate
Front cavity plate
(‘A’ plate)
Rear cavity plate
(‘B’ plate)
Sprue Support plate
puller Ejector retainer
pin plate
Return pin
Ejector plate
Ejector housing
The injection mould is normally described by a variety of criteria, including (1)
number of cavities in the mould; (2) material of construction, e.g., steel, stainless
steel, hardened steel, beryllium copper, chrome-plated aluminum, and epoxy steel;
(3) parting line, e.g., regular, irregular, two-plate mould, and three-plate mould; (4)
method of manufacture, e.g., machining, hobbing, casting, pressure casting,
electroplating, and spark erosion; (5) runner system, e.g., Cold, hot runner and
insulated runner; (6) gating type, e.g., edge, restricted (pinpoint), submarine, sprue,
ring, diaphragm, tab, flash, fan, and multiple; and (7) method of ejection, e.g.,
knockout pins, stripper ring, stripper plate, unscrewing cam, removable insert,
hydraulic core pull, and pneumatic core pull.
Types of Injection Moulds:
Two main types of injection moulds are Cold runner and Hot runner moulds.
A runner is the channel in the mould that conveys the plastic from the barrel of the
injection moulding machine to the part. The runner channel either heated (hot) or non
heated (cold) in above two types of moulds.
Cold Runner Moulds:
The runner is a part of the ejected product and is produced in each cycle. They are
grinded to reuse or scrapped. Moulds are simple and much cheaper than hot runner
moulds. The mould requires less maintenance and less skill to set up and operate.
Colour changes are also very easy, since all of the plastic in the mould is ejected with
each cycle. Common types of Cold Runner Moulds are 2 and 3 plate moulds.
A two plate cold runner mould is the simplest type of mould. It has one parting
plane, and the mould splits into two halves. The runner system must be located on
this parting plane; thus the part can only be gated on its perimeter.
DAVE TECHNICAL SERVICES 100