Page 102 - C:\Users\Adik\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Marketer PPT LR\
P. 102
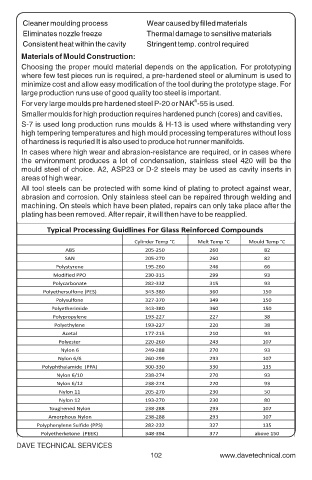
Cleaner moulding process Wear caused by filled materials
Eliminates nozzle freeze Thermal damage to sensitive materials
Consistent heat within the cavity Stringent temp. control required
Materials of Mould Construction:
Choosing the proper mould material depends on the application. For prototyping
where few test pieces run is required, a pre-hardened steel or aluminum is used to
minimize cost and allow easy modification of the tool during the prototype stage. For
large production runs use of good quality too steel is important.
R
For very large moulds pre hardened steel P-20 or NAK -55 is used.
Smaller moulds for high production requires hardened punch (cores) and cavities.
S-7 is used long production runs moulds & H-13 is used where withstanding very
high tempering temperatures and high mould processing temperatures without loss
of hardness is requried It is also used to produce hot runner manifolds.
In cases where high wear and abrasion-resistance are required, or in cases where
the environment produces a lot of condensation, stainless steel 420 will be the
mould steel of choice. A2, ASP23 or D-2 steels may be used as cavity inserts in
areas of high wear.
All tool steels can be protected with some kind of plating to protect against wear,
abrasion and corrosion. Only stainless steel can be repaired through welding and
machining. On steels which have been plated, repairs can only take place after the
plating has been removed. After repair, it will then have to be reapplied.
Typical Processing Guidlines For Glass Reinforced Compounds
Cylinder Temp °C Melt Temp °C Mould Temp °C
ABS 205-250 260 82
SAN 205-270 260 82
Polystyrene 195-260 246 66
Modified PPO 230-315 299 93
Polycarbonate 282-332 315 93
Polyethersulfone (PES) 343-380 360 150
Polysulfone 327-370 349 150
Polyetherimide 343-380 360 150
Polypropylene 193-227 227 38
Polyethylene 193-227 220 38
Acetal 177-215 210 93
Polyester 220-260 243 107
Nylon 6 249-288 270 93
Nylon 6/6 260-299 293 107
Polyphthalamide (PPA) 300-330 330 135
Nylon 6/10 238-274 270 93
Nylon 6/12 238-274 270 93
Nylon 11 205-270 230 50
Nylon 12 193-270 230 80
Toughened Nylon 238-288 293 107
Amorphous Nylon 238-288 293 107
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) 282-232 327 135
Polyetherketone (PEEK) 348-394 377 above 150
DAVE TECHNICAL SERVICES
102