Page 103 - Essential Haematology
P. 103
Chapter 7 Genetic disorders of haemoglobin / 89
This chapter deals with inherited diseases caused by globin (see Table 2.2 ). The major component is
reduced or abnormal synthesis of globin. Mutations haemoglobin A with the molecular structure α 2 β 2 .
in the globin genes are the most prevalent mono- The minor haemoglobins contain γ (fetal Hb or Hb
genic disorders worldwide and aff ect approximately F) or δ (Hb A 2 ) globin chains instead of β chains.
’
7% of the world s population. Th e synthesis In the embryo and fetus, Gower 1, Portland, Gower
of normal haemoglobin in the fetus and adult is 2 and fetal Hb dominate at different stages (Fig.
described first. 7.1 ). The genes for the globin chains occur in two
clusters: ε , γ , δ and β on chromosome 11 and ζ and
α on chromosome 16. Two types of γ chain occur,
Haemoglobin s ynthesis
G γ and A γ , which differ by a glycine or alanine
Normal adult blood contains three types of haemo- amino acid at position 136 in the polypeptide
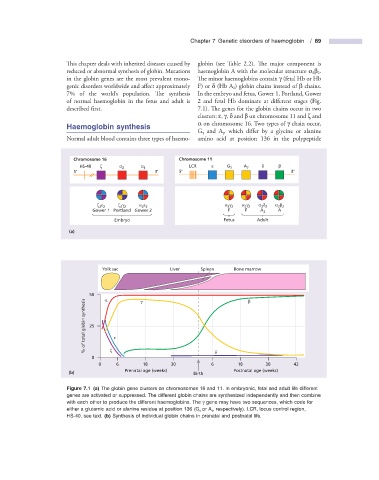
Chromosome 16 Chromosome 11
HS-40 ζ α 2 α 1 LCR ε G γ A γ δ β
5' 3' 5' 3'
ε ζ γ α ε γ α γ α δ α β
ζ 2 2 2 2 2 2 α 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Gower 1 Portland Gower 2 F F A 2 A
Embryo Fetus Adult
(a)
Yolk sac Liver Spleen Bone marrow
50 α γ β
% of total globin synthesis 25 ε
0 ζ δ
0 6 18 30 6 18 30 42
Prenatal age (weeks) Postnatal age (weeks)
(b) Birth
Figure 7.1 (a) The globin gene clusters on chromosomes 16 and 11. In embryonic, fetal and adult life different
genes are activated or suppressed. The different globin chains are synthesized independently and then combine
with each other to produce the different haemoglobins. The γ gene may have two sequences, which code for
either a glutamic acid or alanine residue at position 136 (G γ or A γ , respectively). LCR, locus control region,
HS - 40, see text. (b) Synthesis of individual globin chains in prenatal and postnatal life.