Page 106 - Essential Haematology
P. 106
92 / Chapter 7 Genetic disorders of haemoglobin
α - Thalassaemia s yndromes normal and DNA analysis is needed to be certain
of the diagnosis. Uncommon non - deletional forms
These are usually caused by gene deletions and are
of α - thalassaemia are caused by point mutations
listed in Table 7.2 . As there are normally four copies
producing dysfunction of the genes or rarely by
of the α - globin gene, the clinical severity can be
mutations affecting termination of translation
classifi ed according to the number of genes that are
which give rise to an elongated but unstable chain
missing or inactive. Loss of all four genes com-
(e.g. Hb Constant Spring). Two rare forms of α -
pletely suppresses α - chain synthesis (Fig. 7.4 ) and
thalassaemia are associated with mental retardation.
because the α chain is essential in fetal as well as
They are caused by mutation in a gene on chromo-
in adult haemoglobin this is incompatible with
some 16 (ATR - 16) or on chromosome X (ATR - X)
life and leads to death in utero (hydrops fetalis;
which control the transcription of the α globin and
Fig. 7.5 ). Th ree α gene deletions leads to a moder-
other genes.
ately severe (haemoglobin 7 – 11 g/dL) microcytic,
hypochromic anaemia (Fig. 7.6 ) with splenomegaly.
This is known as Hb H disease because haemo- β - Thalassaemia s yndromes
globin H ( β 4 ) can be detected in red cells of these
β - Thalassaemia m ajor
patients by electrophoresis or in reticulocyte prepa-
rations (Fig. 7.6 ). In fetal life, Hb Barts ( γ 4 ) occurs. This condition occurs on average in one in four
Th e α - thalassaemia traits are caused by loss of offspring if both parents are carriers of the β -
0
one or two genes and are usually not associated with thalassaemia trait. Either no β chain ( β ) or small
+
anaemia, although the mean corpuscular volume amounts ( β ) are synthesized. Excess α chains pre-
(MCV) and mean corpuscular haemoglobin cipitate in erythroblasts and in mature red cells
(MCH) are low and the red cell count is over causing the severe ineffective erythropoiesis and
12
5.5 × 10 /L. Haemoglobin electrophoresis is haemolysis that are typical of this disease. Th e
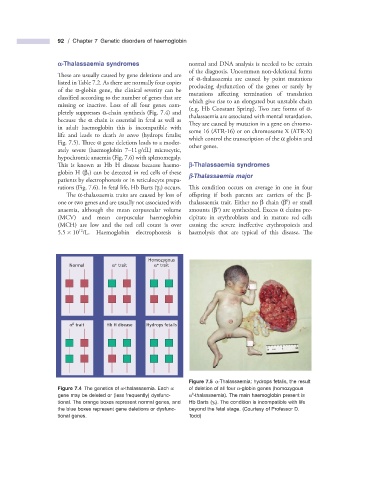
Homozygous
+
+
Normal α trait α trait
0
α trait Hb H disease Hydrops fetalis
Figure 7.5 α - Thalassaemia: hydrops fetalis, the result
Figure 7.4 The genetics of α - thalassaemia. Each α of deletion of all four α - globin genes (homozygous
0
gene may be deleted or (less frequently) dysfunc- α - thalassaemia). The main haemoglobin present is
tional. The orange boxes represent normal genes, and Hb Barts ( γ 4 ). The condition is incompatible with life
the blue boxes represent gene deletions or dysfunc- beyond the fetal stage. (Courtesy of Professor D.
tional genes. Todd)