Page 104 - Essential Haematology
P. 104
90 / Chapter 7 Genetic disorders of haemoglobin
chain. Th e α - chain gene is duplicated and both α A number of other conserved sequences are
genes ( α 1 and α 2 ) on each chromosome are active important in globin synthesis and mutations at
(Fig. 7.1 ). these sites may also give rise to thalassaemia. Th ese
sequences influence gene transcription, ensure its
fidelity, specify sites for the initiation and termina-
Molecular a spects
tion of translation, and ensure the stability of newly
′
All the globin genes have three exons (coding synthesized mRNA. Promoters are found 5 of the
regions) and two introns (non - coding regions whose gene, either close to the initiation site or more dis-
DNA is not represented in the fi nished protein). tally. They are the sites where RNA polymerases
The initial RNA is transcribed from both introns bind and catalyse gene transcription (see Fig. 1.9 ).
′
′
and exons, and from this transcript the RNA Enhancers occur either 5 or 3 to the gene (Fig.
derived from introns is removed by a process known 7.2 ). Enhancers are important in the tissue - specifi c
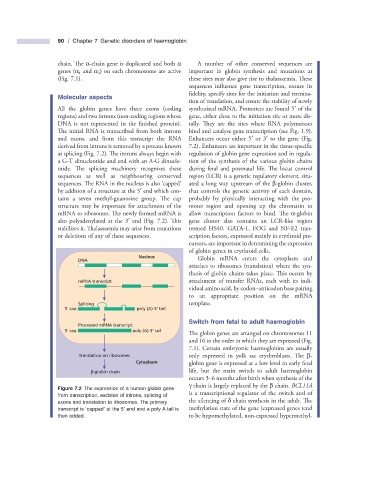
as splicing (Fig. 7.2 ). The introns always begin with regulation of globin gene expression and in regula-
a G - T dinucleotide and end with an A - G dinucle- tion of the synthesis of the various globin chains
otide. The splicing machinery recognizes these during fetal and postnatal life. The locus control
sequences as well as neighbouring conserved region (LCR) is a genetic regulatory element, situ-
‘
sequences. The RNA in the nucleus is also capped ’ ated a long way upstream of the β - globin cluster,
′
by addition of a structure at the 5 end which con- that controls the genetic activity of each domain,
tains a seven methyl - guanosine group. Th e cap probably by physically interacting with the pro-
structure may be important for attachment of the moter region and opening up the chromatin to
mRNA to ribosomes. The newly formed mRNA is allow transcription factors to bind. Th e α - globin
′
also polyadenylated at the 3 end (Fig. 7.2 ). Th is gene cluster also contains an LCR - like region
stabilizes it. Thalassaemia may arise from mutations termed HS40. GATA - 1, FOG and NF - E2 tran-
or deletions of any of these sequences. scription factors, expressed mainly in erythroid pre-
cursors, are important in determining the expression
of globin genes in erythroid cells.
Nucleus
DNA Globin mRNA enters the cytoplasm and
attaches to ribosomes (translation) where the syn-
thesis of globin chains takes place. This occurs by
mRNA transcript attachment of transfer RNAs, each with its indi-
vidual amino acid, by codon – anticodon base pairing
to an appropriate position on the mRNA
Splicing template.
5' cap poly (A)-3' tail
Switch from f etal to a dult h aemoglobin
Processed mRNA transcript
5' cap poly (A)-3' tail
The globin genes are arranged on chromosomes 11
and 16 in the order in which they are expressed (Fig.
7.1 ). Certain embryonic haemoglobins are usually
Translation on ribosomes only expressed in yolk sac erythroblasts. Th e β -
Cytoplasm globin gene is expressed at a low level in early fetal
β-globin chain life, but the main switch to adult haemoglobin
occurs 3 – 6 months after birth when synthesis of the
γ chain is largely replaced by the β chain. BCL11A
Figure 7.2 The expression of a human globin gene
is a transcriptional regulator of the switch and of
from transcription, excision of introns, splicing of
exons and translation to ribosomes. The primary the silencing of δ chain synthesis in the adult. Th e
′
transcript is ‘ capped ’ at the 5 end and a poly A tail is methylation state of the gene (expressed genes tend
then added. to be hypomethylated, non - expressed hypermethyl-