Page 110 - Essential Haematology
P. 110
96 / Chapter 7 Genetic disorders of haemoglobin
commenced in the first year of life and unless the 5 Infections can occur for a variety of reasons.
disease is cured by stem cell transplantantion, In infancy, without adequate transfusion, the
are continued for life. Also iron absorption is anaemic child is prone to bacterial infections.
increased because of low serum hepcidin levels Pneumococcal, Haemophilus and meningococcal
because of release of GDF 15 and TWSG1 from infections are likely if splenectomy has been
early red cell precursors which are increased carried out and prophylactic penicillin is not
because of ineffective erythropoisis. The tests for taken. Yersinia enterocolitica occurs, particularly
iron overload, clinical features (cardiac, hepatic in iron - loaded patients being treated with defer-
and endocrine) and chelation therapy are dis- oxamine; it may cause severe gastroenteritis. Iron
cussed in Chapter 4 . overload also predisposes to baterial infections,
e.g. Klebsiella and fungal infections.Transfusion
of viruses by blood transfusion may occur.
Liver disease in thalassaemia is most fre-
quently a result of hepatitis C but hepatitis B is
also common where the virus is endemic. Human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has been trans-
mitted to some patients by blood transfusion. As
a result of better iron chelation therapy reducing
substantially death from cardiac iron overload,
infections now account for an increasing
proportion of deaths in thalassaemia major in the
UK.
6 Osteoporosis may occur in well - transfused
patients. It is more common in diabetic patients
with endocrine abnormalities and with marrow
expansion resulting from ineffective erythopoiesis.
Laboratory d iagnosis
1 There is a severe hypochromic microcytic
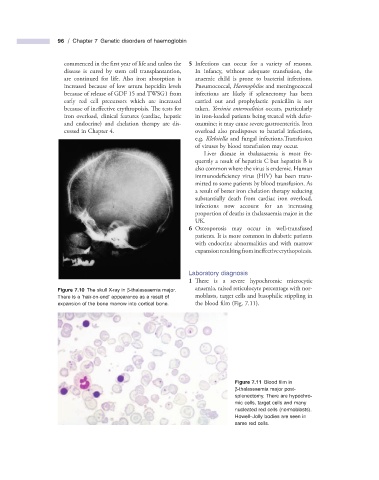
Figure 7.10 The skull X - ray in β - thalassaemia major. anaemia, raised reticulocyte percentage with nor-
There is a ‘ hair - on - end ’ appearance as a result of moblasts, target cells and basophilic stippling in
expansion of the bone marrow into cortical bone. the blood film (Fig. 7.11 ).
Figure 7.11 Blood fi lm in
β - thalassaemia major post -
splenectomy. There are hypochro-
mic cells, target cells and many
nucleated red cells (normoblasts).
Howell – Jolly bodies are seen in
same red cells.