Page 340 - Essential Haematology
P. 340
326 / Chapter 24 Platelets, blood coagulation and haemostasis
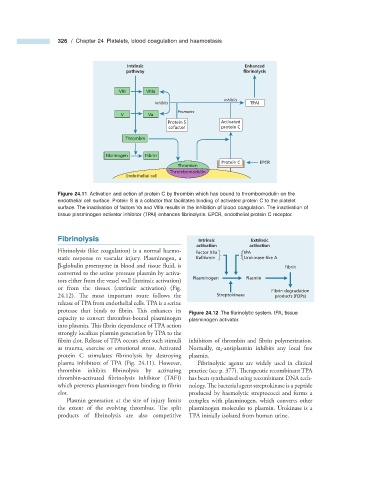
Intrinsic Enhanced
pathway fibrinolysis
VIII VIIIa
Inhibits
Inhibits TPAI
Promotes
V Va
Protein S Activated
cofactor protein C
Thrombin
Fibrinogen Fibrin
Protein C EPCR
Thrombin
Thrombomodulin
Endothelial cell
Figure 24.11 Activation and action of protein C by thrombin which has bound to thrombomodulin on the
endothelial cell surface. Protein S is a cofactor that facilitates binding of activated protein C to the platelet
surface. The inactivation of factors Va and VIIIa results in the inhibition of blood coagulation. The inactivation of
tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor (TPAI) enhances fi brinolysis. EPCR, endothelial protein C receptor.
Fibrinolysis Intrinsic Extrinsic
activation activation
Fibrinolysis (like coagulation) is a normal haemo- Factor XIIa tPA
static response to vascular injury. Plasminogen, a Kallikrein Urokinase-like A
β - globulin proenzyme in blood and tissue fl uid, is Fibrin
converted to the serine protease plasmin by activa-
Plasminogen Plasmin
tors either from the vessel wall (intrinsic activation)
or from the tissues (extrinsic activation) (Fig.
Fibrin degradation
24.12 ). The most important route follows the Streptokinase products (FDPs)
release of TPA from endothelial cells. TPA is a serine
protease that binds to fi brin. This enhances its Figure 24.12 The fi brinolytic system. tPA, tissue
capacity to convert thrombus - bound plasminogen plasminogen activator.
into plasmin. Th is fibrin dependence of TPA action
strongly localizes plasmin generation by TPA to the
fibrin clot. Release of TPA occurs after such stimuli inhibitors of thrombin and fi brin polymerization.
as trauma, exercise or emotional stress. Activated Normally, α 2 - antiplasmin inhibits any local free
protein C stimulates fibrinolysis by destroying plasmin.
plasma inhibitors of TPA (Fig. 24.11 ). However, Fibrinolytic agents are widely used in clinical
thrombin inhibits fibrinolysis by activating practice (see p. 377) . Th erapeutic recombinant TPA
thrombin - activated fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) has been synthesized using recombinant DNA tech-
which prevents plasminogen from binding to fi brin nology. The bacterial agent streptokinase is a peptide
clot. produced by haemolytic streptococci and forms a
Plasmin generation at the site of injury limits complex with plasminogen, which converts other
the extent of the evolving thrombus. Th e split plasminogen molecules to plasmin. Urokinase is a
products of fibrinolysis are also competitive TPA initially isolated from human urine.