Page 408 - Essential Haematology
P. 408
394 / Chapter 28 Haematological changes in systemic disease
Table 28.6 Advantages and disadvantages
of the tests used to monitor the acute phase
response.
Advantages Disadvantages
CRP *
Specifi c test of acute More than one protein
phase protein required to measure
acute (CRP) and
chronic infl ammation
Fast response (6 Costly when assayed
hours) to change in in small numbers
disease activity
High sensitivity – owing Sophisticated
to large incremental equipment and
change antisera required
Can be measured on
stored serum
Small sample
volumes
Automated analysis
ESR and plasma viscosity
Useful in chronic Not sensitive to acute
disease changes ( < 24 hours)
ESR inexpensive, Not specifi c for acute
easy, no electrical phase response
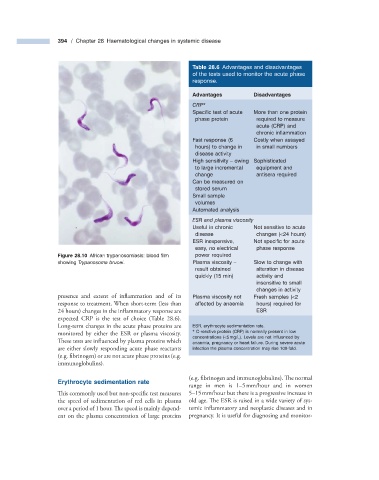
Figure 28.10 African trypanosomiasis: blood fi lm power required
showing Trypanosoma brucei . Plasma viscosity – Slow to change with
result obtained alteration in disease
quickly (15 min) activity and
insensitive to small
changes in activity
presence and extent of inflammation and of its Plasma viscosity not Fresh samples ( < 2
response to treatment. When short - term (less than affected by anaemia hours) required for
24 hours) changes in the inflammatory response are ESR
expected CRP is the test of choice (Table 28.6 ).
Long - term changes in the acute phase proteins are ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
monitored by either the ESR or plasma viscosity. * C - reactive protein (CRP) is normally present in low
concentrations ( < 5 mg/L). Levels are not infl uenced by
These tests are influenced by plasma proteins which anaemia, pregnancy or heart failure. During severe acute
are either slowly responding acute phase reactants infection the plasma concentration may rise 100 - fold.
(e.g. fibrinogen) or are not acute phase proteins (e.g.
immunoglobulins).
(e.g. fibrinogen and immunoglobulins). Th e normal
Erythrocyte s edimentation r ate
range in men is 1 – 5 mm/hour and in women
This commonly used but non - specific test measures 5 – 15 mm/hour but there is a progressive increase in
the speed of sedimentation of red cells in plasma old age. Th e ESR is raised in a wide variety of sys-
over a period of 1 hour. The speed is mainly depend- temic inflammatory and neoplastic diseases and in
ent on the plasma concentration of large proteins pregnancy. It is useful for diagnosing and monitor-