Page 409 - Essential Haematology
P. 409
Chapter 28 Haematological changes in systemic disease / 395
(a) (b)
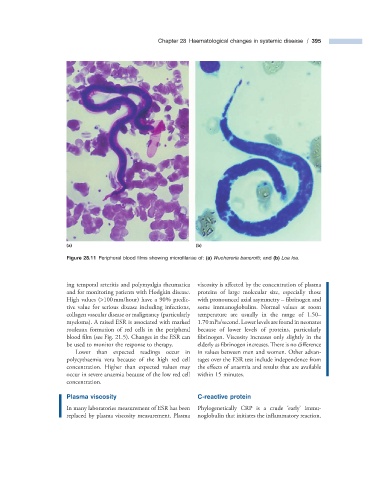
Figure 28.11 Peripheral blood fi lms showing microfi lariae of: (a) Wuchereria bancrofti ; and (b) Loa loa .
ing temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica viscosity is affected by the concentration of plasma
and for monitoring patients with Hodgkin disease. proteins of large molecular size, especially those
High values ( > 100 mm/hour) have a 90% predic- with pronounced axial asymmetry – fi brinogen and
tive value for serious disease including infections, some immunoglobulins. Normal values at room
collagen vascular disease or malignancy (particularly temperature are usually in the range of 1.50 –
myeloma). A raised ESR is associated with marked 1.70 mPa/second. Lower levels are found in neonates
rouleaux formation of red cells in the peripheral because of lower levels of proteins, particularly
blood film (see Fig. 21.5 ). Changes in the ESR can fibrinogen. Viscosity increases only slightly in the
be used to monitor the response to therapy. elderly as fibrinogen increases. There is no diff erence
Lower than expected readings occur in in values between men and women. Other advan-
polycythaemia vera because of the high red cell tages over the ESR test include independence from
concentration. Higher than expected values may the effects of anaemia and results that are available
occur in severe anaemia because of the low red cell within 15 minutes.
concentration.
Plasma v iscosity C - r eactive p rotein
In many laboratories measurement of ESR has been Phylogenetically CRP is a crude early ’ immu-
‘
replaced by plasma viscosity measurement. Plasma noglobulin that initiates the infl ammatory reaction.