Page 413 - Essential Haematology
P. 413
Chapter 29 Blood transfusion / 399
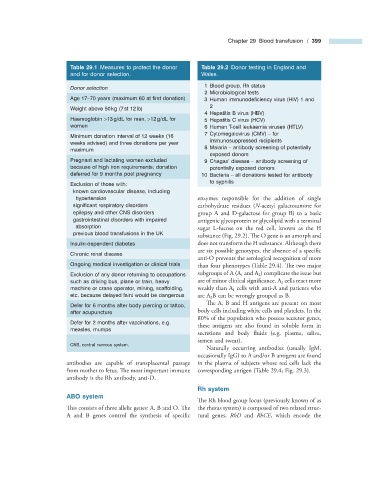
Table 29.1 Measures to protect the donor Table 29.2 Donor testing in England and
and for donor selection. Wales.
1 Blood group, Rh status
Donor selection
2 Microbiological tests
Age 17 – 70 years (maximum 60 at fi rst donation) 3 Human immunodefi ciency virus (HIV) 1 and
2
Weight above 50 kg (7 st 12 lb)
4 Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Haemoglobin > 13 g/dL for men, > 12 g/dL for 5 Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
women 6 Human T - cell leukaemia viruses (HTLV)
7 Cytomegalovirus (CMV) – for
Minimum donation interval of 12 weeks (16
immunosuppressed recipients
weeks advised) and three donations per year
8 Malaria – antibody screening of potentially
maximum
exposed donors
Pregnant and lactating women excluded 9 Chagas ’ disease – antibody screening of
because of high iron requirements; donation potentially exposed donors
deferred for 9 months post pregnancy 10 Bacteria – all donations tested for antibody
to syphilis
Exclusion of those with:
known cardiovascular disease, including
hypertension enzymes responsible for the addition of single
signifi cant respiratory disorders carbohydrate residues ( N - acetyl galactosamine for
epilepsy and other CNS disorders group A and D - galactose for group B) to a basic
gastrointestinal disorders with impaired antigenic glycoprotein or glycolipid with a terminal
absorption sugar L - fucose on the red cell, known as the H
previous blood transfusions in the UK
substance (Fig. 29.2 ). The O gene is an amorph and
Insulin - dependent diabetes does not transform the H substance. Although there
are six possible genotypes, the absence of a specifi c
Chronic renal disease
anti - O prevents the serological recognition of more
Ongoing medical investigation or clinical trials than four phenotypes (Table 29.4 ). Th e two major
Exclusion of any donor returning to occupations subgroups of A (A 1 and A 2 ) complicate the issue but
such as driving bus, plane or train, heavy are of minor clinical signifi cance. A 2 cells react more
machine or crane operator, mining, scaffolding, weakly than A 1 cells with anti - A and patients who
etc. because delayed faint would be dangerous are A 2 B can be wrongly grouped as B.
The A, B and H antigens are present on most
Defer for 6 months after body piercing or tattoo,
after acupuncture body cells including white cells and platelets. In the
80% of the population who possess secretor genes,
Defer for 2 months after vaccinations, e.g. these antigens are also found in soluble form in
measles, mumps
secretions and body fluids (e.g. plasma, saliva,
semen and sweat).
CNS, central nervous system.
Naturally occurring antibodies (usually IgM,
occasionally IgG) to A and/or B antigens are found
antibodies are capable of transplacental passage in the plasma of subjects whose red cells lack the
from mother to fetus. The most important immune corresponding antigen (Table 29.4 ; Fig. 29.3 ).
antibody is the Rh antibody, anti - D.
R h s ystem
ABO s ystem
The Rh blood group locus (previously known of as
This consists of three allelic genes: A, B and O. Th e the rhesus system) is composed of two related struc-
A and B genes control the synthesis of specifi c tural genes, RhD and RhCE , which encode the