Page 416 - Essential Haematology
P. 416
402 / Chapter 29 Blood transfusion
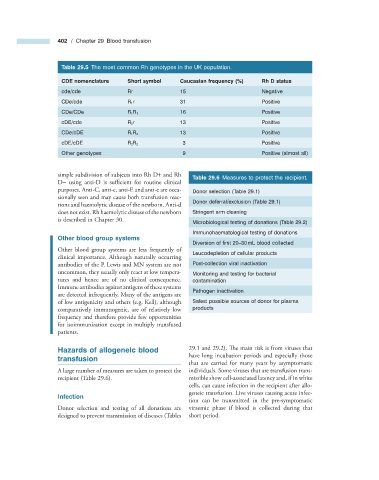
Table 29.5 The most common R h genotypes in the UK population.
CDE nomenclature Short symbol Caucasian frequency (%) Rh D status
cde/cde Rr 15 Negative
CDe/cde R 1 r 31 Positive
CDe/CDe R 1 R 1 16 Positive
cDE/cde R 2 r 13 Positive
CDe/cDE R 1 R 2 13 Positive
cDE/cDE R 2 R 2 3 Positive
Other genotypes 9 Positive (almost all)
simple subdivision of subjects into Rh D + and Rh
Table 29.6 Measures to protect the recipient.
D − using anti - D is sufficient for routine clinical
purposes. Anti - C, anti - c, anti - E and anti - e are occa- Donor selection (Table 29.1 )
sionally seen and may cause both transfusion reac-
Donor deferral/exclusion (Table 29.1 )
tions and haemolytic disease of the newborn. Anti - d
does not exist. Rh haemolytic disease of the newborn Stringent arm cleaning
is described in Chapter 30 .
Microbiological testing of donations (Table 29.2 )
Immunohaematological testing of donations
Other b lood g roup s ystems
Diversion of fi rst 20 – 30 mL blood collected
Other blood group systems are less frequently of
Leucodepletion of cellular products
clinical importance. Although naturally occurring
antibodies of the P, Lewis and MN system are not Post - collection viral inactivation
uncommon, they usually only react at low tempera- Monitoring and testing for bacterial
tures and hence are of no clinical consequence. contamination
Immune antibodies against antigens of these systems
Pathogen inactivation
are detected infrequently. Many of the antigens are
of low antigenicity and others (e.g. Kell), although Safest possible sources of donor for plasma
comparatively immunogenic, are of relatively low products
frequency and therefore provide few opportunities
for isoimmunization except in multiply transfused
patients.
Hazards of a llogeneic b lood 29.1 and 29.2 ). The main risk is from viruses that
have long incubation periods and especially those
t ransfusion
that are carried for many years by asymptomatic
A large number of measures are taken to protect the individuals. Some viruses that are transfusion trans-
recipient (Table 29.6 ). missible show cell - associated latency and, if in white
cells, can cause infection in the recipient after allo-
geneic transfusion. Live viruses causing acute infec-
Infection
tion can be transmitted in the pre - symptomatic
Donor selection and testing of all donations are viraemic phase if blood is collected during that
designed to prevent transmission of diseases (Tables short period.