Page 418 - Essential Haematology
P. 418
404 / Chapter 29 Blood transfusion
also excluded. Rare transmission occurs when the nents are now excluded as blood donors in the UK.
donor is incubating the infection but has not yet No screening tests for prions are yet available.
developed the antibody that is detected in the labo-
ratory test used (window period transmission).
Techniques in b lood g roup
s erology
Human T - c ell l eukaemias v iruses
Human T - cell leukaemias virus type I (HTLVI) is The most important technique is based on the
associated with adult T - cell leukaemia or tropical agglutination of red blood cells. Saline agglutina-
spastic paraparesis. Human T - cell leukaemia virus tion is important in detecting IgM antibodies,
type II (HLTVII) has no known association with usually at room temperature and 4 ° C (e.g. anti - A,
any clinical condition. Screening for both is manda- anti - B; Fig. 29.3 ). Addition of colloid to the incu-
tory in the UK despite the low prevalence, approxi- bation or proteolytic enzyme treatment of red cells
mately 1 in 50 000 untested donors. increases the sensitivity of the indirect antiglobulin
test (see below), as does low ionic strength saline.
Cytomegalovirus These latter methods can detect a range of IgG
Post - infusion cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is antibodies.
usually subclinical but may give an infectious The antiglobulin test is a fundamental and
mononucleosis syndrome. Immunosuppressed indi- widely used test in both blood group serology and
viduals are at risk of pneumonitis and a potentially general immunology. Antihuman globulin (AHG)
fatal disease. These are premature babies ( < 1500 g), is produced in animals following the injection of
stem cell and other organ transplant recipients, human globulin, purified complement or specifi c
patients who have received alemtuzumab (anti - immunoglobulin (e.g. IgG, IgA or IgM). Monoclonal
CD52, Campath) and pregnant women (the fetus preparations are also now available. When AHG is
is at risk). For such recipients, CMV negative blood added to human red cells coated with immunoglob-
or blood components must be given if they are ulin or complement components, agglutination of
CMV negative. the red cells indicates a positive test (Fig. 29.5 ).
The antiglobulin test may be either direct or
Other i nfections indirect. The direct antiglobulin test is used for
Syphilis is more likely to be transmitted by platelets
(stored at room temperature) than blood (stored at
4 ° C). However, all donations are tested. Malarial
parasites are viable in blood stored at 4 ° C, so in
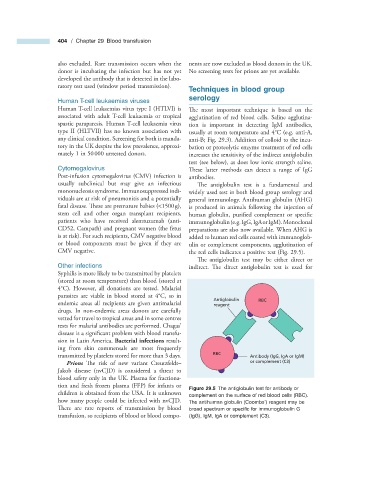
Antiglobulin RBC
endemic areas all recipients are given antimalarial reagent
drugs. In non - endemic areas donors are carefully
vetted for travel to tropical areas and in some centres
tests for malarial antibodies are performed. Chagas ’
disease is a significant problem with blood transfu-
sion in Latin America. Bacterial infections result-
ing from skin commensals are most frequently
transmitted by platelets stored for more than 3 days. RBC Antibody (IgG, IgA or IgM)
Prions The risk of new variant Creutzfeldt – or complement (C3)
Jakob disease (nvCJD) is considered a threat to
blood safety only in the UK. Plasma for fractiona-
tion and fresh frozen plasma (FFP) for infants or
Figure 29.5 The antiglobulin test for antibody or
children is obtained from the USA. It is unknown complement on the surface of red blood cells (RBC).
how many people could be infected with nvCJD. The antihuman globulin (Coombs ’ ) reagent may be
There are rare reports of transmission by blood broad spectrum or specifi c for immunoglobulin G
transfusion, so recipients of blood or blood compo- (IgG), IgM, IgA or complement (C3).