Page 420 - Essential Haematology
P. 420
406 / Chapter 29 Blood transfusion
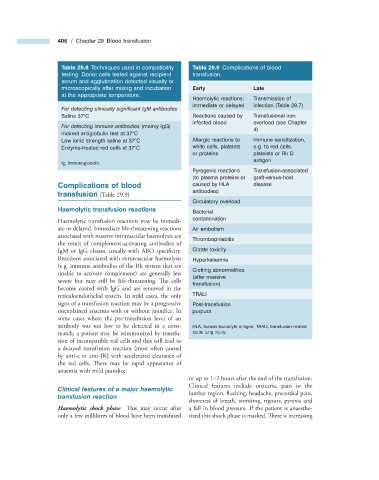
Table 29.8 Techniques used in compatibility Table 29.9 Complications of blood
testing. Donor cells tested against recipient transfusion.
serum and agglutination detected visually or
microscopically after mixing and incubation Early Late
at the appropriate temperature.
Haemolytic reactions: Transmission of
immediate or delayed infection (Table 29.7 )
For detecting clinically signifi cant IgM antibodies
Saline 37 ° C Reactions caused by Transfusional iron
infected blood overload (see Chapter
For detecting immune antibodies (mainly IgG)
4 )
Indirect antiglobulin test at 37 ° C
Low ionic strength saline at 37 ° C Allergic reactions to Immune sensitization,
Enzyme - treated red cells at 37 ° C white cells, platelets e.g. to red cells,
or proteins platelets or Rh D
antigen
Ig, immunoglobulin.
Pyrogenic reactions Transfusion - associated
(to plasma proteins or graft - versus - host
Complications of b lood caused by HLA disease
antibodies)
t ransfusion (Table 29.9 )
Circulatory overload
Haemolytic t ransfusion r eactions Bacterial
Haemolytic transfusion reactions may be immedi- contamination
ate or delayed. Immediate life - threatening reactions Air embolism
associated with massive intravascular haemolysis are
Thrombophlebitis
the result of complement - activating antibodies of
IgM or IgG classes, usually with ABO specifi city. Citrate toxicity
Reactions associated with extravascular haemolysis Hyperkalaemia
(e.g. immune antibodies of the Rh system that are
Clotting abnormalities
unable to activate complement) are generally less
(after massive
severe but may still be life - threatening. Th e cells
transfusion)
become coated with IgG and are removed in the
reticuloendothelial system. In mild cases, the only TRALI
signs of a transfusion reaction may be a progressive Post - transfusion
unexplained anaemia with or without jaundice. In purpura
some cases where the pre - transfusion level of an
antibody was too low to be detected in a cross - HLA, human leucocyte antigen; TRALI, transfusion - related
match, a patient may be reimmunized by transfu- acute lung injury.
sion of incompatible red cells and this will lead to
a delayed transfusion reaction (most often caused
by anti - c or anti - JK) with accelerated clearance of
the red cells. There may be rapid appearance of
anaemia with mild jaundice.
or up to 1 – 2 hours after the end of the transfusion.
Clinical features include urticaria, pain in the
Clinical f eatures of a m ajor h aemolytic
lumbar region, flushing, headache, precordial pain,
t ransfusion r eaction
shortness of breath, vomiting, rigours, pyrexia and
Haemolytic shock phase Th is may occur after a fall in blood pressure. If the patient is anaesthe-
only a few millilitres of blood have been transfused tized this shock phase is masked. There is increasing