Page 417 - Essential Haematology
P. 417
Chapter 29 Blood transfusion / 403
Individual i nfections Human i mmunodefi ciency v irus
Hepatitis This can be transmitted by cells or plasma. Male
Donors with a history of hepatitis are deferred for homosexuals, bisexuals, intravenous drug users and
12 months. If there is a history of jaundice, they prostitutes are excluded, as are their sexual partners
can be accepted if markers for hepatitis B virus and partners of haemophiliacs. Inhabitants of large
(HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) are negative areas of sub - Saharan Africa and South - East Asia
(Table 29.7 ). where HIV infection is particularly common are
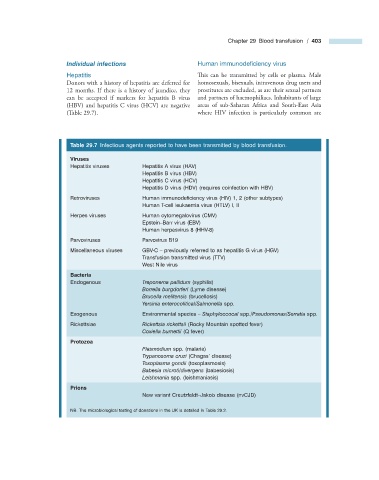
Table 29.7 Infectious agents reported to have been transmitted by blood transfusion.
Viruses
Hepatitis viruses Hepatitis A virus (HAV)
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
Hepatitis D virus (HDV) (requires coinfection with HBV)
Retroviruses Human immunodefi ciency virus (HIV) 1, 2 (other subtypes)
Human T - cell leukaemia virus (HTLV) I, II
Herpes viruses Human cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Epstein – Barr virus (EBV)
Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV - 8)
Parvoviruses Parvovirus B19
Miscellaneous viruses GBV - C – previously referred to as hepatitis G virus (HGV)
Transfusion transmitted virus (TTV)
West Nile virus
Bacteria
Endogenous Treponema pallidum (syphilis)
Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease)
Brucella melitensis (brucellosis)
Yersinia enterocolitical/Salmonella spp.
Exogenous Environmental species – Staphyloccocal spp./ Pseudomonas / Serratia spp.
Rickettsiae Rickettsia rickettsii (Rocky Mountain spotted fever)
Coxiella burnettii (Q fever)
Protozoa
Plasmodium spp. (malaria)
Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas ’ disease)
Toxoplasma gondii (toxoplasmosis)
Babesia microti/divergens (babesiosis)
Leishmania spp. (leishmaniasis)
Prions
New variant Creutzfeldt – Jakob disease (nvCJD)
NB. The microbiological testing of donations in the UK is detailed in Table 29.2 .