Page 412 - Essential Haematology
P. 412
398 / Chapter 29 Blood transfusion
FFP for clinical use
FFP for fractionation Albumin
Gammaglobulin
Fresh plasma Cryoprecipitate* Specific antiviral
+ cryosupernatant immunglobulins
Anti-D
Coagulation
Platelets factors
(store room
Whole blood Buffy coat temperature)
± (pool from
leucodepletion 4 donors)
Buffy coat residue
– discarded
Red cell
concentrate
Optimal additive solution (OAS)
e.g. SAGM
Red cells in OAS
(store at 4°C)
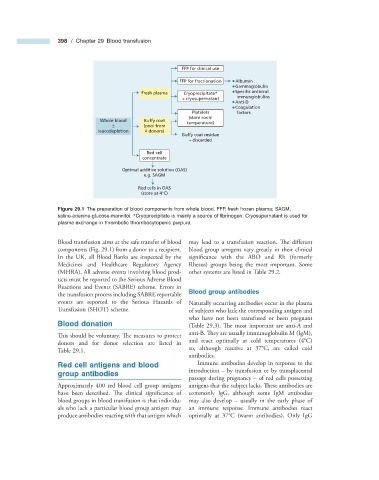
Figure 29.1 The preparation of blood components from whole blood. FFP, fresh frozen plasma; SAGM,
saline - adenine - glucose - mannitol. * Cryoprecipitate is mainly a source of fi brinogen. Cryosupernatant is used for
plasma exchange in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Blood transfusion aims at the safe transfer of blood may lead to a transfusion reaction. Th e diff erent
components (Fig. 29.1 ) from a donor to a recipient. blood group antigens vary greatly in their clinical
In the UK, all Blood Banks are inspected by the significance with the ABO and Rh (formerly
Medicines and Healthcare Regulatory Agency Rhesus) groups being the most important. Some
(MHRA). All adverse events involving blood prod- other systems are listed in Table 29.2 .
ucts must be reported to the Serious Adverse Blood
Reactions and Events (SABRE) scheme. Errors in
the transfusion process including SABRE reportable Blood g roup a ntibodies
events are reported to the Serious Hazards of Naturally occurring antibodies occur in the plasma
Transfusion (SHOT) scheme. of subjects who lack the corresponding antigen and
who have not been transfused or been pregnant
Blood d onation (Table 29.3 ). The most important are anti - A and
anti - B. They are usually immunoglobulin M (IgM),
This should be voluntary. The measures to protect
and react optimally at cold temperatures (4 ° C)
donors and for donor selection are listed in
so, although reactive at 37 ° C, are called cold
Table 29.1 .
antibodies.
Red c ell a ntigens and b lood Immune antibodies develop in response to the
introduction – by transfusion or by transplacental
g roup a ntibodies
passage during pregnancy – of red cells possessing
Approximately 400 red blood cell group antigens antigens that the subject lacks. These antibodies are
have been described. The clinical signifi cance of commonly IgG, although some IgM antibodies
blood groups in blood transfusion is that individu- may also develop – usually in the early phase of
als who lack a particular blood group antigen may an immune response. Immune antibodies react
produce antibodies reacting with that antigen which optimally at 37 ° C (warm antibodies). Only IgG