Page 998 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 998
984 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
Sensitization phase: Effector phase: Cytokines Effects
initial contact secondary contact
with antigen with antigen
IL-8 Chemotaxis
IL-1 IL-2 receptor T DTH MIF of macrophages
MCP
Allergen
CD4 IL-2 IL-2 Activation of
macrophages
IFN-γ (increased
IL-1 TNF-β phagocytic
Proliferation and and microbicidal
TCR T helper differentiation
cell (TH1) activities)
Class II MHC IL-2
Antigen-presenting Induction of
myelopoiesis of
cell (eg, macrophage, IL-3 macrophage and
GM-CSF
Langerhans cell) neutrophil precursors
Macrophage IL-8 Chemotaxis and
Memory T DTH TNF-α extravasation of
MIP macrophages
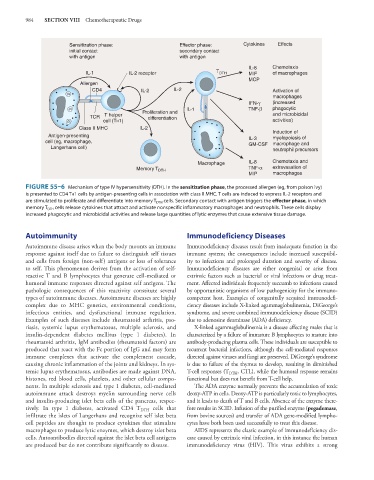
FIGURE 55–6 Mechanism of type IV hypersensitivity (DTH). In the sensitization phase, the processed allergen (eg, from poison ivy)
is presented to CD4 Th1 cells by antigen-presenting cells in association with class II MHC. T cells are induced to express IL-2 receptors and
are stimulated to proliferate and differentiate into memory T DTH cells. Secondary contact with antigen triggers the effector phase, in which
memory T DTH cells release cytokines that attract and activate nonspecific inflammatory macrophages and neutrophils. These cells display
increased phagocytic and microbicidal activities and release large quantities of lytic enzymes that cause extensive tissue damage.
Autoimmunity Immunodeficiency Diseases
Autoimmune disease arises when the body mounts an immune Immunodeficiency diseases result from inadequate function in the
response against itself due to failure to distinguish self tissues immune system; the consequences include increased susceptibil-
and cells from foreign (non-self) antigens or loss of tolerance ity to infections and prolonged duration and severity of disease.
to self. This phenomenon derives from the activation of self- Immunodeficiency diseases are either congenital or arise from
reactive T and B lymphocytes that generate cell-mediated or extrinsic factors such as bacterial or viral infections or drug treat-
humoral immune responses directed against self antigens. The ment. Affected individuals frequently succumb to infections caused
pathologic consequences of this reactivity constitute several by opportunistic organisms of low pathogenicity for the immuno-
types of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases are highly competent host. Examples of congenitally acquired immunodefi-
complex due to MHC genetics, environmental conditions, ciency diseases include X-linked agammaglobulinemia, DiGeorge’s
infectious entities, and dysfunctional immune regulation. syndrome, and severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID)
Examples of such diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, pso- due to adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
riasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and X-linked agammaglobulinemia is a disease affecting males that is
insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (type 1 diabetes). In characterized by a failure of immature B lymphocytes to mature into
rheumatoid arthritis, IgM antibodies (rheumatoid factors) are antibody-producing plasma cells. These individuals are susceptible to
produced that react with the Fc portion of IgG and may form recurrent bacterial infections, although the cell-mediated responses
immune complexes that activate the complement cascade, directed against viruses and fungi are preserved. DiGeorge’s syndrome
causing chronic inflammation of the joints and kidneys. In sys- is due to failure of the thymus to develop, resulting in diminished
temic lupus erythematosus, antibodies are made against DNA, T-cell responses (T DTH , CTL), while the humoral response remains
histones, red blood cells, platelets, and other cellular compo- functional but does not benefit from T-cell help.
nents. In multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes, cell-mediated The ADA enzyme normally prevents the accumulation of toxic
autoimmune attack destroys myelin surrounding nerve cells deoxy-ATP in cells. Deoxy-ATP is particularly toxic to lymphocytes,
and insulin-producing islet beta cells of the pancreas, respec- and it leads to death of T and B cells. Absence of the enzyme there-
tively. In type 1 diabetes, activated CD4 T DTH cells that fore results in SCID. Infusion of the purified enzyme (pegademase,
infiltrate the islets of Langerhans and recognize self islet beta from bovine sources) and transfer of ADA gene-modified lympho-
cell peptides are thought to produce cytokines that stimulate cytes have both been used successfully to treat this disease.
macrophages to produce lytic enzymes, which destroy islet beta AIDS represents the classic example of immunodeficiency dis-
cells. Autoantibodies directed against the islet beta cell antigens ease caused by extrinsic viral infection, in this instance the human
are produced but do not contribute significantly to disease. immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This virus exhibits a strong