Page 997 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 997
CHAPTER 55 Immunopharmacology 983
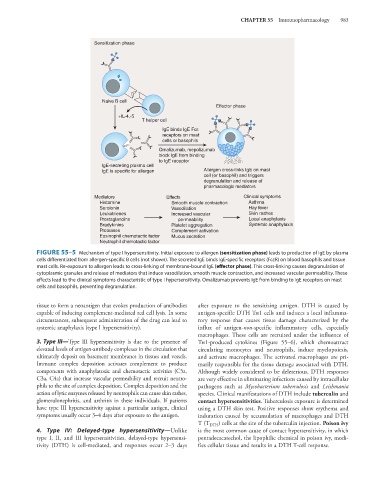
Sensitization phase
Naive B cell
Effector phase
+IL-4,-5
T helper cell
IgE binds IgE Fcε
receptors on mast
cells or basophils
Omalizumab, mepolizumab
block IgE from binding
to IgE receptor
IgE-secreting plasma cell
IgE is specific for allergen Allergen cross-links IgE on mast
cell (or basophil) and triggers
degranulation and release of
pharmacologic mediators
Mediators Effects Clinical symptoms
Histamine Smooth muscle contraction Asthma
Serotonin Vasodilation Hay fever
Leukotrienes Increased vascular Skin rashes
Prostaglandins permeability Local anaphylaxis
Bradykinins Platelet aggregation Systemic anaphylaxis
Proteases Complement activation
Eosinophil chemotactic factor Mucus secretion
Neutrophil chemotactic factor
FIGURE 55–5 Mechanism of type I hypersensitivity. Initial exposure to allergen (sensitization phase) leads to production of IgE by plasma
cells differentiated from allergen-specific B cells (not shown). The secreted IgE binds IgE-specific receptors (FcεR) on blood basophils and tissue
mast cells. Re-exposure to allergen leads to cross-linking of membrane-bound IgE (effector phase). This cross-linking causes degranulation of
cytoplasmic granules and release of mediators that induce vasodilation, smooth muscle contraction, and increased vascular permeability. These
effects lead to the clinical symptoms characteristic of type I hypersensitivity. Omalizumab prevents IgE from binding to IgE receptors on mast
cells and basophils, preventing degranulation.
tissue to form a neoantigen that evokes production of antibodies after exposure to the sensitizing antigen. DTH is caused by
capable of inducing complement-mediated red cell lysis. In some antigen-specific DTH Th1 cells and induces a local inflamma-
circumstances, subsequent administration of the drug can lead to tory response that causes tissue damage characterized by the
systemic anaphylaxis (type I hypersensitivity). influx of antigen-non-specific inflammatory cells, especially
macrophages. These cells are recruited under the influence of
3. Type III—Type III hypersensitivity is due to the presence of Th1-produced cytokines (Figure 55–6), which chemoattract
elevated levels of antigen-antibody complexes in the circulation that circulating monocytes and neutrophils, induce myelopoiesis,
ultimately deposit on basement membranes in tissues and vessels. and activate macrophages. The activated macrophages are pri-
Immune complex deposition activates complement to produce marily responsible for the tissue damage associated with DTH.
components with anaphylatoxic and chemotactic activities (C5a, Although widely considered to be deleterious, DTH responses
C3a, C4a) that increase vascular permeability and recruit neutro- are very effective in eliminating infections caused by intracellular
phils to the site of complex deposition. Complex deposition and the pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Leishmania
action of lytic enzymes released by neutrophils can cause skin rashes, species. Clinical manifestations of DTH include tuberculin and
glomerulonephritis, and arthritis in these individuals. If patients contact hypersensitivities. Tuberculosis exposure is determined
have type III hypersensitivity against a particular antigen, clinical using a DTH skin test. Positive responses show erythema and
symptoms usually occur 3–4 days after exposure to the antigen. induration caused by accumulation of macrophages and DTH
T (T DTH ) cells at the site of the tuberculin injection. Poison ivy
4. Type IV: Delayed-type hypersensitivity—Unlike is the most common cause of contact hypersensitivity, in which
type I, II, and III hypersensitivities, delayed-type hypersensi- pentadecacatechol, the lipophilic chemical in poison ivy, modi-
tivity (DTH) is cell-mediated, and responses occur 2–3 days fies cellular tissue and results in a DTH T-cell response.