Page 995 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 995
CHAPTER 55 Immunopharmacology 981
Opsonized
bacteria
Lysosome
Macrophage
Antigen- B lymphocyte
presenting
cell
Class I MHC
IL-1, 6, 23 peptide
TGF-β IL-1
T lymphocyte
IL-17 TH IL-2
IL-22 Class II MHC
Th17
Peptide
IL-2 IL-2
IL-10
IL-4, IL-5
TH1
IFN-γ TH2
IFN-γ
TNF-β
IFN-γ Differentiation Immunoglobulin
Proliferation classes
IgG
IgM
IgA
IgD
Activated Activated Activated IgE
macrophage NK cell cytotoxic T cell
(kills bacteria) (kills virus- (kills tumor Memory B cells
infected cells cells and Plasma cells
and tumor virus-infected
cells) cells)
Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity
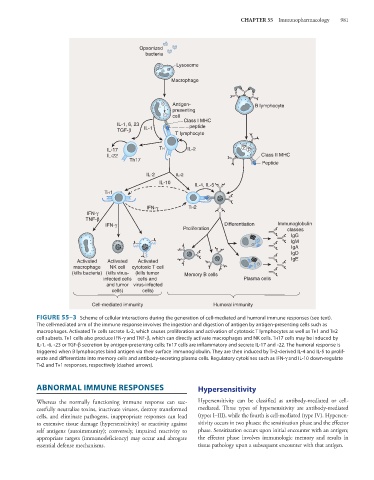
FIGURE 55–3 Scheme of cellular interactions during the generation of cell-mediated and humoral immune responses (see text).
The cell-mediated arm of the immune response involves the ingestion and digestion of antigen by antigen-presenting cells such as
macrophages. Activated Th cells secrete IL-2, which causes proliferation and activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes as well as Th1 and Th2
cell subsets. Th1 cells also produce IFN-γ and TNF-β, which can directly activate macrophages and NK cells. Th17 cells may be induced by
IL-1, -6, -23 or TGF-β secretion by antigen-presenting cells; Th17 cells are inflammatory and secrete IL-17 and -22. The humoral response is
triggered when B lymphocytes bind antigen via their surface immunoglobulin. They are then induced by Th2-derived IL-4 and IL-5 to prolif-
erate and differentiate into memory cells and antibody-secreting plasma cells. Regulatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-10 down-regulate
Th2 and Th1 responses, respectively (dashed arrows).
ABNORMAL IMMUNE RESPONSES Hypersensitivity
Whereas the normally functioning immune response can suc- Hypersensitivity can be classified as antibody-mediated or cell-
cessfully neutralize toxins, inactivate viruses, destroy transformed mediated. Three types of hypersensitivity are antibody-mediated
cells, and eliminate pathogens, inappropriate responses can lead (types I–III), while the fourth is cell-mediated (type IV). Hypersen-
to extensive tissue damage (hypersensitivity) or reactivity against sitivity occurs in two phases: the sensitization phase and the effector
self antigens (autoimmunity); conversely, impaired reactivity to phase. Sensitization occurs upon initial encounter with an antigen;
appropriate targets (immunodeficiency) may occur and abrogate the effector phase involves immunologic memory and results in
essential defense mechanisms. tissue pathology upon a subsequent encounter with that antigen.