Page 996 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 996
982 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
A
Bacteria
Epitope
Antigen-
binding Hinge
region region
C 1 V H
Complementarity- H
determining
region (CDR)
–S-S– –S-S– –S-S– V L
–S-S–
C H 2 C L
Fc region
C H 3
B
C
Fc receptor Opsonization
Complement
activation
Macrophage
Bacterial lysis
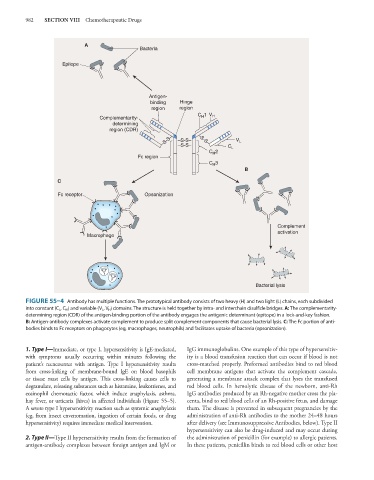
FIGURE 55–4 Antibody has multiple functions. The prototypical antibody consists of two heavy (H) and two light (L) chains, each subdivided
into constant (C L , C H ) and variable (V L , V H ) domains. The structure is held together by intra- and interchain disulfide bridges. A: The complementarity-
determining region (CDR) of the antigen-binding portion of the antibody engages the antigenic determinant (epitope) in a lock-and-key fashion.
B: Antigen-antibody complexes activate complement to produce split complement components that cause bacterial lysis. C: The Fc portion of anti-
bodies binds to Fc receptors on phagocytes (eg, macrophages, neutrophils) and facilitates uptake of bacteria (opsonization).
1. Type I—Immediate, or type I, hypersensitivity is IgE-mediated, IgG immunoglobulins. One example of this type of hypersensitiv-
with symptoms usually occurring within minutes following the ity is a blood transfusion reaction that can occur if blood is not
patient’s reencounter with antigen. Type I hypersensitivity results cross-matched properly. Preformed antibodies bind to red blood
from cross-linking of membrane-bound IgE on blood basophils cell membrane antigens that activate the complement cascade,
or tissue mast cells by antigen. This cross-linking causes cells to generating a membrane attack complex that lyses the transfused
degranulate, releasing substances such as histamine, leukotrienes, and red blood cells. In hemolytic disease of the newborn, anti-Rh
eosinophil chemotactic factor, which induce anaphylaxis, asthma, IgG antibodies produced by an Rh-negative mother cross the pla-
hay fever, or urticaria (hives) in affected individuals (Figure 55–5). centa, bind to red blood cells of an Rh-positive fetus, and damage
A severe type I hypersensitivity reaction such as systemic anaphylaxis them. The disease is prevented in subsequent pregnancies by the
(eg, from insect envenomation, ingestion of certain foods, or drug administration of anti-Rh antibodies to the mother 24–48 hours
hypersensitivity) requires immediate medical intervention. after delivery (see Immunosuppressive Antibodies, below). Type II
hypersensitivity can also be drug-induced and may occur during
2. Type II—Type II hypersensitivity results from the formation of the administration of penicillin (for example) to allergic patients.
antigen-antibody complexes between foreign antigen and IgM or In these patients, penicillin binds to red blood cells or other host