Page 376 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 376
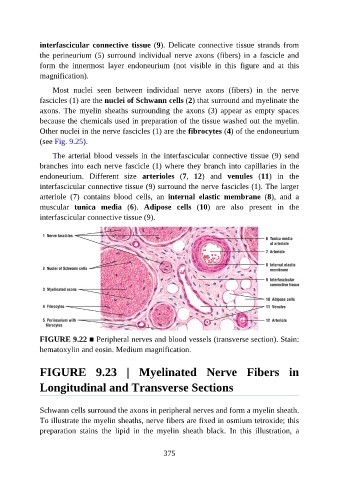
interfascicular connective tissue (9). Delicate connective tissue strands from
the perineurium (5) surround individual nerve axons (fibers) in a fascicle and
form the innermost layer endoneurium (not visible in this figure and at this
magnification).
Most nuclei seen between individual nerve axons (fibers) in the nerve
fascicles (1) are the nuclei of Schwann cells (2) that surround and myelinate the
axons. The myelin sheaths surrounding the axons (3) appear as empty spaces
because the chemicals used in preparation of the tissue washed out the myelin.
Other nuclei in the nerve fascicles (1) are the fibrocytes (4) of the endoneurium
(see Fig. 9.25).
The arterial blood vessels in the interfascicular connective tissue (9) send
branches into each nerve fascicle (1) where they branch into capillaries in the
endoneurium. Different size arterioles (7, 12) and venules (11) in the
interfascicular connective tissue (9) surround the nerve fascicles (1). The larger
arteriole (7) contains blood cells, an internal elastic membrane (8), and a
muscular tunica media (6). Adipose cells (10) are also present in the
interfascicular connective tissue (9).
FIGURE 9.22 ■ Peripheral nerves and blood vessels (transverse section). Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. Medium magnification.
FIGURE 9.23 | Myelinated Nerve Fibers in
Longitudinal and Transverse Sections
Schwann cells surround the axons in peripheral nerves and form a myelin sheath.
To illustrate the myelin sheaths, nerve fibers are fixed in osmium tetroxide; this
preparation stains the lipid in the myelin sheath black. In this illustration, a
375